Busbars are integral to the backbone of electrical systems, ensuring the efficient and reliable transmission of electrical power. As industries evolve and power demands increase, the need for precision in busbar fabrication becomes even more critical. Whether used in industrial switchgear, power distribution panels, or custom applications, the fabrication of busbars requires a delicate balance of material selection, cutting-edge machinery, and expert craftsmanship. However, manufacturers face numerous challenges in delivering high-quality busbars that meet strict performance standards. From achieving tight tolerances to minimizing defects, overcoming these hurdles is essential for maintaining the longevity and efficiency of electrical systems. This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of busbar fabrication, providing insights into the materials, processes, and technological advancements that drive the industry forward.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Busbar Fabrication: A Comprehensive Guide
Busbars have become essential components in electrical engineering, serving as critical conductors in modern power distribution systems. The busbar fabrication process requires precision, expertise, and advanced equipment to ensure optimal performance and reliability. From industrial equipment sheet metal enclosures to high-voltage switchgear panels, properly fabricated busbars form the backbone of electrical infrastructure.
According to Machine Design, the global busbar market is projected to exceed $20 billion by 2027, reflecting the growing demand for efficient power distribution solutions. However, the busbar manufacturing process presents numerous challenges that manufacturers must navigate to deliver high-quality products.
If you’d rather listen than read, feel free to play the audio file below for the rest of this article.
Understanding the Busbar Production Landscape
The journey from raw copper or aluminum to a finished busbar involves multiple critical stages. Industry research shows that busbar production efficiency directly impacts overall electrical system performance and longevity.
Material Selection in Copper Busbar Fabrication
Copper busbar fabrication remains the gold standard for high-performance applications due to copper’s superior conductivity (58 MS/m compared to aluminum’s 37 MS/m). The choice between copper and aluminum involves critical trade-offs that every busbar technician must understand.
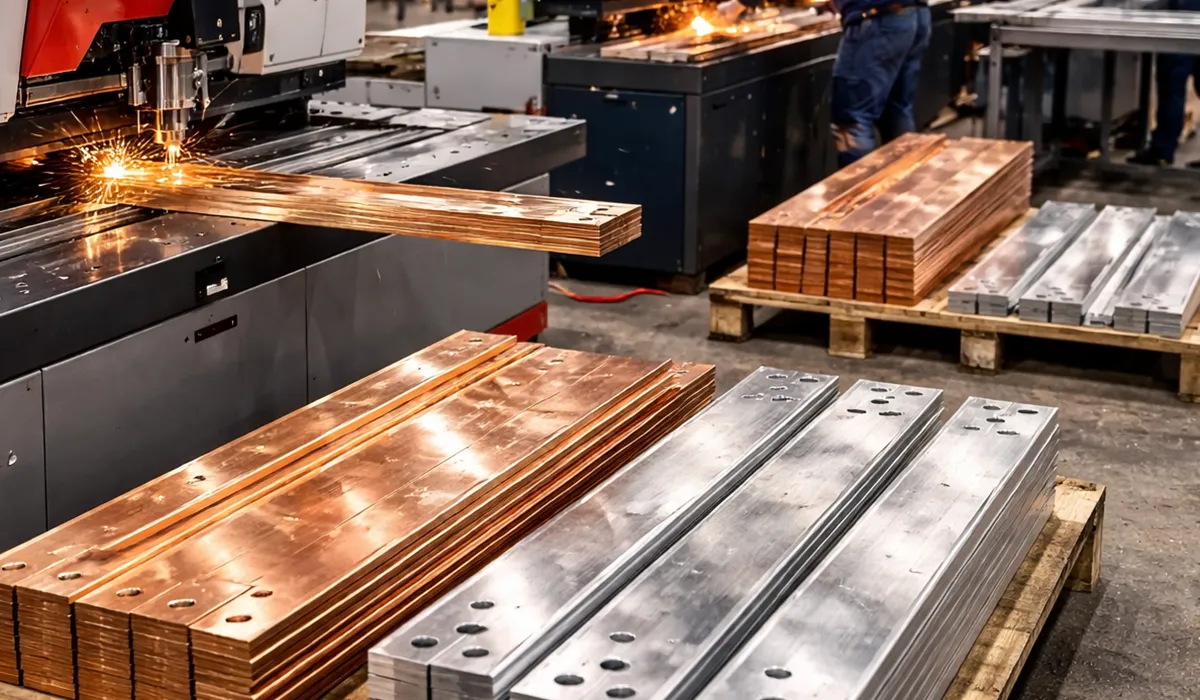

Material properties significantly affect the fabrication process. For example, Schneider Electric’s manufacturing facility in Lexington, Kentucky, reported a 23% reduction in material waste after implementing precision laser cut bending sheet metal enclosures technology for their aluminum busbar production line.
| Material Properties Comparison | SPECIFICATION |
|---|---|
| 58 MS/m (Copper) vs 37 MS/m (Aluminum) | Conductivity |
| 8.96 g/cm³ (Copper) vs 2.70 g/cm³ (Aluminum) | Density |
| 16.5 µm/(m·K) vs 23.1 µm/(m·K) | Thermal Expansion |
| 220 MPa (Copper) vs 90 MPa (Aluminum) | Tensile Strength |
| 50,000+ hours (properly maintained) | Mean Time Between Failures |
Critical Challenges in Modern Busbar Manufacturing
Research from Electrical Contractor Magazine identifies five primary obstacles that impact production quality and efficiency.
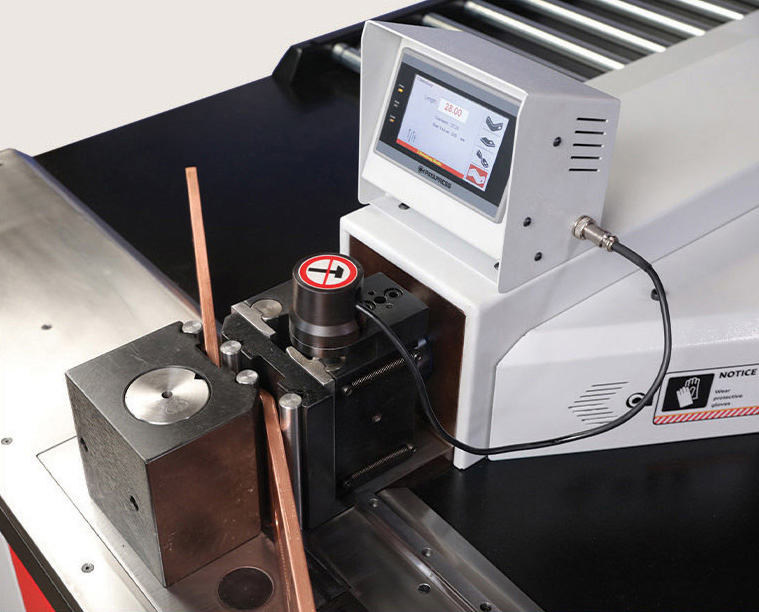
Precision Requirements and Dimensional Accuracy
Maintaining tolerances within ±0.1mm is crucial for proper fitting in electrical enclosures. ABB’s German facility implemented advanced busbar fabrication machines that reduced dimensional errors by 89%, achieving copper busbar fabrication standards.
A formed busbar fabricator must account for spring-back effects during bending operations. For instance, when bending 10mm copper busbar at 90 degrees, typical spring-back ranges from 2-4 degrees, requiring over-bending compensation.
Bending and Forming Complexities
The busbar bending process introduces stress concentrations that can compromise structural integrity. According to Metal Forming Magazine, improper bend radius calculations account for 34% of all busbar failures.
Real-world example: Eaton Corporation’s Cleveland plant reduced bending-related defects from 12% to 1.8% by implementing CNC-controlled busbar bending machines with automated radius calculation.
Welding and Joint Integrity
Joint resistance directly impacts system efficiency. Siemens’ testing revealed that poorly executed welds can increase contact resistance by 400%, generating excessive heat and reducing mean time between failures.
For critical applications, ultrasonic welding has proven superior to traditional methods. General Electric’s switchgear division reported 99.7% joint reliability using ultrasonic welding compared to 94.2% with conventional TIG welding.
Surface Treatment and Corrosion Protection
Proper surface finishing extends busbar lifespan significantly. Industry studies show that tin-plated copper busbars demonstrate 15-year service life in harsh environments versus 8 years for untreated copper.
Advanced Solutions and Equipment Integration
Modern busbar fabrication workflows leverage integrated machinery to address traditional challenges. Automation World reports that manufacturers using multi-function equipment achieve 45% higher throughput.
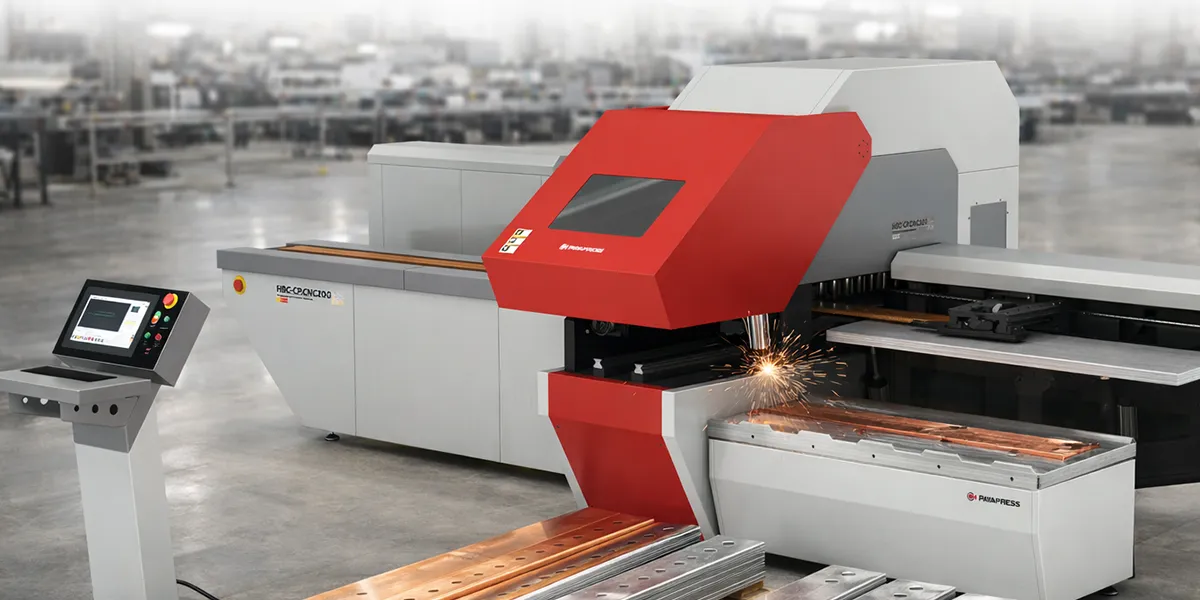

CNC Busbar Processing Systems
The implementation of advanced busbar processing machinery has revolutionized production efficiency. Rittal AG’s investment in CNC systems reduced setup time from 45 minutes to 6 minutes per product changeover.
Multi-Function Busbar Machines
Combining multiple functions in single units eliminates material handling errors. Legrand’s French facility achieved 99.4% first-pass yield using 3-in-1 machines that cut, punch, and bend in one operation.
| Performance Improvement Metrics | CATEGORY |
|---|---|
| 89% reduction in dimensional errors | Precision |
| 45% increase in production throughput | Efficiency |
| 87% decrease in setup time | Flexibility |
| 23% reduction in material waste | Sustainability |
| 99.7% joint reliability achievement | Quality |
Quality Control and Testing Protocols
Quality Magazine emphasizes that comprehensive testing at each production stage is non-negotiable. Leading manufacturers implement:
Material Verification: Spectroscopic analysis ensures material composition meets specifications. Phoenix Contact discovered 7% of incoming copper stock failed to meet C11000 standards, highlighting the importance of incoming inspection.
Dimensional Inspection: Coordinate measuring machines (CMM) verify critical dimensions. Global switchgear manufacturers using CMM inspection report 96% reduction in field failures.
Electrical Testing: Contact resistance measurement identifies potential failure points. Industry standard: less than 10 microohms per joint for copper busbars.
Non-Destructive Testing Methods
Ultrasonic testing detects internal defects without damaging products. Mitsubishi Electric’s quality control system uses automated ultrasonic inspection to achieve 99.9% defect detection rates.
For a comprehensive understanding of Global switchgear manufacturers, we highly recommend reviewing this article.
Workforce Development and Technical Training
Despite automation advances, skilled busbar technicians remain essential. Industry Week reports that companies investing in comprehensive training programs experience 34% lower defect rates.
Successful training programs include:
– CNC programming for busbar processing equipment
– Material science fundamentals
– Quality control methodologies
– Safety protocols for electrical component manufacturing
– Troubleshooting and preventive maintenance
Supply Chain Optimization for Busbar Production
Effective supply chain management ensures consistent material quality and availability. Supply Chain Management Review identifies three critical strategies:
Supplier Partnerships: Long-term relationships with certified copper and aluminum suppliers reduce quality variability. Schneider Electric maintains strategic partnerships with five primary material suppliers, ensuring 99.2% on-time delivery.
Inventory Management: Just-in-time systems balanced with safety stock prevent production delays while minimizing carrying costs.
Market Intelligence: Tracking commodity prices enables strategic purchasing. Copper price fluctuations of 30% within six months make timing crucial for cost control.
If you are looking for more information about Supply chain optimization, it is recommended not to miss reading this article.
Sustainability in Busbar Manufacturing
Environmental considerations increasingly influence busbar manufacturing process design. Environmental Leader reports that leading manufacturers achieve 85% material recycling rates.
Sustainable practices include:
– Recycling copper and aluminum scrap from cutting and punching operations
– Implementing energy-efficient equipment reducing power consumption by 40%
– Using water-based surface treatments instead of hazardous chemicals
– Optimizing material nesting to minimize waste
Future Trends in Busbar Fabrication Technology
The evolution of busbar technology continues with Industry 4.0 integration. Manufacturing.net predicts that AI-driven quality control will become standard by 2026.
Emerging technologies include:
– IoT sensors monitoring equipment performance in real-time
– Predictive maintenance reducing unplanned downtime by 70%
– Digital twin technology for process optimization
– Additive manufacturing for complex busbar geometries
– Automated inspection using machine vision systems
Conclusion: Excellence in Busbar Manufacturing
Overcoming challenges in busbar fabrication requires strategic integration of advanced equipment, skilled workforce, rigorous quality control, and sustainable practices. As demonstrated by industry leaders like ABB, Schneider Electric, and Siemens, investing in modern fabrication technology and comprehensive training programs delivers measurable improvements in quality, efficiency, and profitability.
The future of busbar production lies in smart manufacturing principles—combining automation, data analytics, and human expertise to achieve unprecedented levels of precision and reliability. Manufacturers who embrace these advances position themselves to meet growing demands for efficient, sustainable electrical infrastructure while maintaining competitive advantages in an evolving market.
Whether producing standard copper busbars for distribution panels or custom-engineered solutions for specialized applications, success depends on understanding material properties, mastering fabrication techniques, implementing robust quality systems, and continuously improving processes through technology adoption and workforce development.