In today’s industrial world, the standardization of safety for switchgear and busbar systems is not only a legal requirement but also a technical necessity to protect users and ensure stable processes. Standards for switchgear and busbar systems are a combination of processes, procedures, and visual work instructions that optimize task execution. These standards form an important foundation for continuous improvement in any company, avoiding mistakes and delays from complicated applications. They also often result in the development of norms and certifications, such as ISO standards, certifications, or emission guidelines.
In this article, we will examine the role of IEC, UL, and CE standards in the context of switchgear and busbar systems. It will explain how these standards for switchgear and busbar systems influence the safety, efficiency, and market acceptance of products. Understanding critical parameters such as current density copper busbar ratings, IEC 61439 requirements for enclosed switchgear, and the ongoing UL 489i IEC harmonization efforts is essential for professionals working with electrical distribution systems. It is important to note that this article serves as a technical guide and does not replace detailed research on official standards or legal advice.
Alternatively, an audio version of this article is available below for your convenience.
What Are International Standards for Switchgear and Busbar Systems?
International IEC standards reflect the global consensus and the accumulated knowledge of thousands of technical experts, who are delegated by their countries to participate in the IEC. They provide instructions, guidelines, rules, or definitions used to design, manufacture, install, test, certify, maintain, and repair electrical and electronic devices and systems.
However, standards for switchgear and busbar systems not only play a role in preventing errors but also significantly contribute to the efficiency and innovative strength of companies. By implementing and adhering to standards, companies can not only ensure the safety and quality of their products but also optimize their production processes and develop new technological solutions. Standards for switchgear and busbar systems create uniform conditions that enable companies to use resources more efficiently, reduce downtime, and better leverage innovation potential.
IEC standards regulate not only quality but also safety requirements, which are of particular importance for standards for switchgear and busbar systems. They help researchers understand the value of innovations and enable manufacturers to produce products with consistent quality and performance. When considering copper busbar current carrying capacity in enclosed switchgear IEC 61439 applications, engineers must carefully evaluate the typical current density copper busbar enclosed switchgear IEC standards to ensure safe and efficient operation. International IEC standards are always used by technical experts; they are voluntary and based on the international consensus of experts from many countries.
Electrical Standards, Codes, and Safety – The Entire Framework of Standards for Switchgear and Busbar Systems
IEC Standards
IEC stands for the International Electrotechnical Commission, a global standards organization for electrical engineering and electronics, based in Geneva. Some standards are jointly developed with the ISO (International Organization for Standardization). Together with ITU, the ISO and IEC form the World Standards Cooperation.
A typical example of IEC standardization is “IEC 60364,” which focuses on electrical low-voltage installations and is the central standard for building construction and electrical installations. Among the various IEC standards for electrical engineering, two are particularly relevant for switchgear and busbar systems: IEC 61439 and IEC 62271-200. These standards address critical aspects including IEC 61439 temperature rise limits for busbars and proper copper current density specifications.

UL Standards
UL standards are safety standards developed by the US organization Underwriters Laboratories (UL) to ensure the safety and functionality of products in the North American market. Products meeting these standards receive a UL label, indicating their approval and essential for distribution in the US. In Canada, additional certifications from the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) or a special cUL mark may be required. The UL 489i harmonization with IEC represents a significant step toward global alignment of circuit breaker standards, making it easier for manufacturers to design products that meet both North American and international requirements. Additionally, UL 1558 online resources provide comprehensive guidance on metal-enclosed switchgear requirements.
National Electrical Code (NEC)
The National Electrical Code (NEC), also known as NFPA 70, is a safety standard in the United States. The NEC covers legal regulations that are mandatory in various countries and govern electrical safety in buildings and installations. Although the NEC does not directly target switchgear and busbar systems, it is essential for electrical installation in buildings and their safety.
ANSI Standards
These set guidelines for electrical installations. The standard is recognized by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). It is part of the standards and codes published by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) under the name ANSI/NFPA 70.
CE Marking
The letters “CE” appear on many products sold in the expanded internal market of the European Economic Area (EEA). They mean that the products sold in the EEA have been tested and meet high safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
Since April 20, 2016, new European regulations have applied to manufacturers, importers, and traders of low-voltage equipment, especially the Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU, which governs devices and components with external connections that carry electrical voltage between 50 and 1,000 V (AC) or 75 and 1,500 V (DC). This ensures that these products are both safe and reliable during operation and meet all necessary protection measures.
Additionally, the Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive 2014/30/EU applies to low-voltage equipment, as it concerns devices and systems that cause or are affected by electromagnetic interference. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for the market approval of low-voltage equipment in the EU.
If this article has been valuable, for further detailed and accurate information on topic CE Marking, we suggest reading the related article
IEC Electrical Standards for Low-Voltage (LV) and Medium-Voltage (MV) Switchgear
IEC as a Global Reference for Electrical Standards
IEC is the leading international organization developing global standards for electrical devices and systems, particularly for switchgear and busbar systems. The adoption of IEC standards is widespread worldwide, including countries like Australia and India.
Understanding how to optimize switchgear performance is crucial for ensuring the long-term reliability of electrical systems. This article provides key insights into optimizing switchgear systems to improve efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance safety. Learn more about switchgear optimization and how it benefits your operations.
IEC 61439: Low-Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear Assemblies
The IEC 61439 standard applies to low-voltage assemblies up to 1,000 V AC and represents a comprehensive framework for ensuring safety and performance in electrical distribution systems.
- Scope: This standard concerns the planning and manufacturing of low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies, primarily used in commercial and industrial plants where reliable and safe power distribution is required. It defines the term “Assembly” as a complete switchgear or control unit. Key aspects include the distinction between Original Equipment Manufacturer and Assembly Manufacturer, as well as design and routine verification. Other critical design aspects include thermal performance, short-circuit withstand strength, and creepage and clearance distances. For busbars, the selection of cross-sectional areas and the quality of the connection according to IEC 61439 busbar current carrying capacity table copper 415V specifications are crucial. Engineers must also consider the IEC 61439 rated diversity factor for main busbar when designing distribution systems to ensure adequate capacity during peak demand periods. When working with high-capacity systems such as copper busbar current carrying capacity enclosed switchgear IEC 61439 6300A installations, proper thermal management and current density copper busbar IEC 61439 enclosed calculations become paramount to prevent overheating and ensure long-term reliability. If you found this article useful, reading an article on topic IEC 61439 is recommended for more specialized information.
- Practical Applications: Typical applications include the installation of low-voltage switchgear in office buildings, manufacturing plants, and data centers where secure and efficient electricity distribution must be ensured. The standard ensures that these systems meet required safety standards and operate reliably under different conditions. Understanding the current density copper busbar IEC 61439 enclosed switchgear parameters helps engineers select appropriate busbar sizes for specific applications, considering factors such as ambient temperature, ventilation, and load profiles.
Busbar systems are essential components in power distribution within switchboards, ensuring the safe and efficient delivery of electrical power. This guide delves into the different types of busbar systems used in switchboards and their role in maintaining system reliability. Explore busbar systems to understand their integration within electrical setups.

IEC 62271-200: Medium-Voltage Switchgear in Metal Enclosures
This standard concerns the planning and operation of medium-voltage switchgear housed in metal enclosures, covering voltages from 1 kV to 52 kV AC.
- Scope: IEC 62271-200 applies to medium-voltage switchgear housed in metal enclosures for voltage ratings from 1 kV to 52 kV AC. It includes key design and safety guidelines for these systems, ensuring proper insulation coordination and arc-flash protection measures that are critical for personnel safety.
- Practical Applications: Medium-voltage switchgear according to IEC 62271-200 is found in power supply networks, industrial plants with high electrical power, and distribution stations. They are particularly used in substations and power distribution plants to ensure reliable electricity distribution in cities and industrial areas. The standard addresses specific concerns related to busbar design in medium-voltage applications, where proper material selection and joint design are essential for minimizing contact resistance and preventing hotspots.
If this article has assisted you, reading an article focused on topic IEC 61439 Designs Verification will offer more extensive information.
Understanding Current Density and Thermal Management in Busbar Systems
One of the most critical aspects of busbar system design is managing current density copper busbar ratings to prevent excessive temperature rise and ensure safe operation. The typical current density copper busbar enclosed switchgear IEC standards typically recommend values between 0.8 to 1.4 A/mm² for continuous operation, though this varies based on several factors including ambient temperature, ventilation conditions, and the configuration of the enclosure.
When engineers design systems according to IEC 61439 temperature rise limits busbars copper current density specifications, they must consider the maximum permissible temperature rise above ambient conditions. The standard typically allows for a temperature rise of 50-70K depending on the specific component and its location within the assembly. For enclosed switchgear, these limits become even more stringent due to reduced heat dissipation capabilities compared to open-air installations.
The relationship between current density and temperature rise is nonlinear, meaning that small increases in current can lead to disproportionately large increases in temperature. This is why the IEC 61439 busbar current carrying capacity table copper 415V provides detailed derating factors for various installation conditions. Engineers must also account for the skin effect at higher frequencies and the proximity effect when multiple busbars are installed close together, both of which can significantly impact the effective copper busbar current carrying capacity enclosed switchgear IEC 61439 6300A systems.
UL Standards for Low-Voltage Switchgear in North America
Discover how busbars work harmoniously within switchgear systems to conduct electricity efficiently. This article highlights the importance of well-designed busbars in achieving optimal electrical flow in industrial settings. Gain a deeper understanding of switchgear harmony and its role in electrical distribution
UL 891: Low-Voltage Switchboards
UL 891 is a safety standard from UL Solutions (formerly Underwriters Laboratories) for low-voltage switchgear used in commercial and light industrial environments for safe power distribution in switchgear and busbar systems. These devices serve as central points for controlling and distributing electrical power and protect against disruptions. They use hard-wired components such as UL 489i or UL 1066 circuit breakers to ensure a dead-front design for increased safety. The ongoing UL 489i harmonization with IEC standards represents an important evolution in the industry, as it seeks to align North American circuit breaker requirements with international practices, reducing the burden on manufacturers who serve global markets while maintaining the high safety standards that UL is known for.
If this article has been helpful, we encourage you to read the article on topic Resistor for a deeper understanding of the subject.
UL 1558: Metal Enclosed Switchgear with Circuit Breakers
UL 1558 is a safety standard for metal-enclosed low-voltage switchgear with circuit breakers up to 1,000 V AC. Compared to UL 891, UL 1558 has higher safety and performance requirements, including better short-circuit strength, complete compartmentalization, and improved arc flash protection measures. These advanced features make UL 1558 especially suitable for demanding industrial applications, manufacturing plants, and data centers, while UL 891 is mainly used in commercial and light industrial sectors. Resources for documentation provide detailed guidance on testing procedures, temperature rise limits, and short-circuit ratings that complement the understanding of IEC 61439 requirements.
UL 891 vs UL 1558 – Functional Differences
UL 891 applies to switchboards up to 600 V AC and is intended for commercial and light industrial applications. It sets basic safety requirements for low-voltage switchgear. UL 1558 refers to metal-enclosed switchgear up to 1,000 V AC and requires higher safety standards, such as larger distances, complete compartmentalization, and improved arc flash protection, making it suitable for demanding industrial applications. These differences make UL 1558 especially important for switchgear and busbar systems used in challenging environments, such as large manufacturing plants or data centers.
The evolution toward UL 489i IEC harmonization reflects the industry’s recognition that global standardization benefits both manufacturers and end users. By aligning testing methods and performance criteria, the harmonization effort aims to create circuit breakers that meet the rigorous requirements of both UL and IEC standards, facilitating international trade and reducing the need for duplicate testing and certification. This harmonization is particularly important for enclosed switchgear applications where circuit breakers must interface seamlessly with other components designed to different standards.
The Role of Diversity Factors in Busbar System Design
When designing electrical distribution systems, engineers must consider the IEC 61439 rated diversity factor for main busbar to avoid over-sizing equipment while ensuring adequate capacity. The diversity factor recognizes that not all connected loads operate simultaneously at their maximum rated capacity. This principle allows for more economical designs without compromising safety or reliability.
The rated diversity factor typically ranges from 0.6 to 1.0 depending on the type of installation and the nature of the connected loads. For example, in a large office building, the diversity factor might be around 0.7, acknowledging that lighting, HVAC systems, and office equipment operate on different schedules and rarely reach peak demand simultaneously. However, in critical applications such as data centers or hospitals, the diversity factor approaches 1.0 to ensure sufficient capacity during all operating conditions.
Understanding the proper application of diversity factors becomes crucial when determining the appropriate copper busbar current carrying capacity enclosed switchgear IEC 61439 6300A for a specific installation. An incorrectly applied diversity factor can lead to either oversized equipment (increasing cost unnecessarily) or undersized equipment (creating safety hazards and potential system failures). The IEC 61439 busbar current carrying capacity table copper 415V provides guidance on how to properly apply these factors in conjunction with current density calculations.
CE Marking for Switchgear and Busbar Fabrication Machines
This article reveals the essential aspects of switchgear systems that ensure reliable power distribution in any industrial setup. By focusing on both the mechanical and electrical components, it provides insights into how switchgear functions under varying conditions. Explore switchgear secrets to unlock the intricacies of electrical distribution systems.
Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC
The Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC sets out basic safety requirements for machines and machinery products, including busbar fabrication machines. It covers risk assessment, protective devices, and emergency stop systems to ensure that machines can be safely operated. These requirements are particularly important for standards for switchgear and busbar systems to ensure their safe use and reliability.
Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
The Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU governs safety requirements for electrical equipment operating within voltage ranges from 50 to 1,000 V AC or 75 to 1,500 V DC. It particularly concerns low-voltage switchgear and electrical components of machines, ensuring their safe use within the European internal market and aligning the standards for switchgear and busbar systems with European safety regulations.
EMC Directive 2014/30/EU
The EMC Directive 2014/30/EU sets requirements for the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) of electrical equipment to ensure that they do not cause interference nor be affected by it. This is particularly important for electronic switchgear and busbar systems, as electromagnetic interference can severely impact functionality and safety.
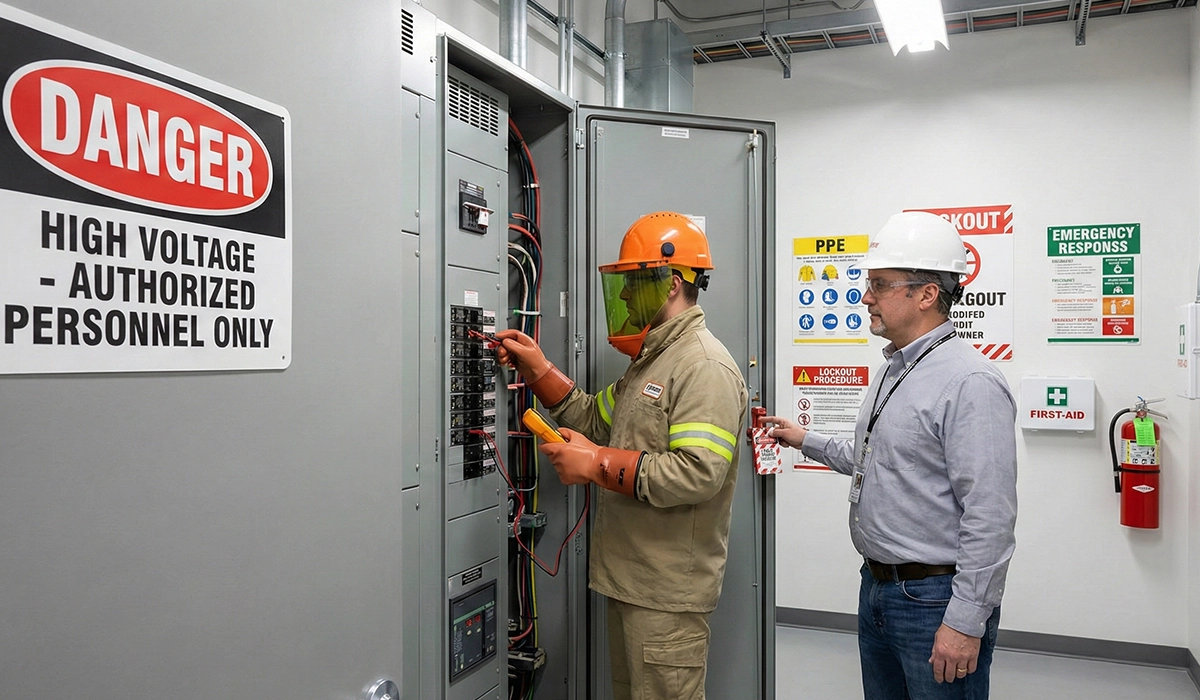

Electrical Safety Standards and Occupational Safety
Overview of Electrical Safety Standards
Electrical safety standards are crucial for designing devices, work methods, and safety measures in the environment. They ensure the safety of personnel and equipment, prevent downtime, ensure compliance with legal requirements, and improve operational efficiency. Electrical safety plays a central role in electrical planning and should not be neglected. An important reference is OSHA standards in the US, which are closely linked with standards like NFPA 70 to ensure high safety requirements for switchgear and busbar systems.
When working with high-capacity systems, understanding the typical current density copper busbar enclosed switchgear IEC standards helps maintenance personnel identify potential problem areas before they develop into critical failures. Thermal imaging surveys can reveal hotspots where actual current density exceeds design values, often due to loose connections, corrosion, or unanticipated load growth. Regular monitoring ensures that IEC 61439 temperature rise limits are not exceeded during normal operation.
Personal Protective Equipment: Safety Shoes and Insulating Mats
Safety standards for shoes and insulating mats play a crucial role in preventing electric shocks and arc flash accidents. Insulating mats provide a barrier between the floor and the user, minimizing the risk of electrical accidents. Safety shoes with insulating properties protect the feet from electrical hazards by preventing direct contact with live parts and reducing the risk of injury from electric shocks, which is vital for the safety of individuals working with switchgear and busbar systems.
Consequences of Ignoring Safety Standards
Ignoring safety standards can lead to severe dangers such as electric shocks, burns, and equipment damage. These incidents can cause not only physical injuries but also significant legal consequences, including liability and heavy fines. Adhering to safety standards is therefore essential to minimize the risk of accidents and meet legal requirements, especially for switchgear and busbar systems, which are indispensable in many industries. Failure to properly calculate current density copper busbar ratings or to respect IEC 61439 temperature rise limits busbars copper current density specifications can result in catastrophic failures, including fire hazards and complete system shutdowns.
Practical Considerations for International Compliance
For manufacturers serving global markets, navigating the landscape of international standards presents both challenges and opportunities. The ongoing UL 489i IEC harmonization initiative exemplifies the industry’s movement toward greater alignment between regional standards. However, significant differences remain, particularly in testing methodologies and performance criteria.
When designing enclosed switchgear for international markets, engineers must often satisfy multiple standards simultaneously. For instance, a switchboard destined for both North American and European markets must comply with both UL 1558 (or UL 891) and IEC 61439 requirements. This dual compliance affects numerous design parameters, including copper busbar current carrying capacity, short-circuit ratings, temperature rise limits, and physical dimensions.
The IEC 61439 busbar current carrying capacity table copper 415V provides specific guidance for European voltage levels, while North American applications typically operate at different voltages (208V, 480V, etc.). Engineers must carefully adapt their designs to account for these voltage differences and their impact on current density copper busbar IEC 61439 enclosed calculations. Additionally, the rated diversity factor for main busbar may be interpreted differently under various regional codes, requiring careful documentation and justification of design choices.
Conclusion
Standards for switchgear and busbar systems play a central role in electrical engineering by ensuring the safety, efficiency, and reliability of systems and devices. International standards such as IEC, UL, and CE provide clear guidelines for the design, manufacturing, and operation of switchgear and busbar systems, helping to minimize risks such as electric shocks, short circuits, or failures.
Understanding critical parameters such as current density copper busbar ratings, IEC 61439 temperature rise limits, and the typical current density copper busbar enclosed switchgear IEC values enables engineers to design safer and more efficient systems. The ongoing evolution of standards, including the UL 489i IEC harmonization efforts and the comprehensive guidance available through UL 1558 online resources, continues to improve global alignment while maintaining rigorous safety requirements.
The application of the IEC 61439 rated diversity factor for main busbar and proper use of the IEC 61439 busbar current carrying capacity table copper 415V ensures that systems are neither under-designed (creating safety hazards) nor over-designed (wasting resources). For high-capacity installations such as copper busbar current carrying capacity enclosed switchgear IEC 61439 6300A systems, meticulous attention to these standards prevents costly failures and ensures reliable long-term operation.
Additionally, standards for switchgear and busbar systems contribute to international trade capability by allowing manufacturers to develop products that are globally recognized and compatible. In an increasingly globalized and technologically advanced industry, adherence to standards is essential to safely implement innovations and ensure long-term success. The convergence of international standards through initiatives like UL 489i harmonization with IEC represents an important step toward reducing technical barriers to trade while maintaining the high safety levels that protect personnel and equipment worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Role Does IEC Play in Safety and International Trade?
IEC standardizations ensure performance, efficiency, and safety conditions for products and systems for switchgear and busbar systems. Furthermore, IEC standards facilitate international trade by defining uniform requirements that manufacturers worldwide must meet, including specifications for current density copper busbar IEC 61439 enclosed switchgear applications. This reduces technical trade barriers and promotes free trade between different countries and regions.
How Does the IEC Standardization Process Work?
The IEC standardization process follows a multi-stage, consensus-based procedure. In this process, technical experts worldwide work in working groups to develop international standards for electrical engineering and electronics. Drafts are published for comment, and national committees vote on the final adoption to ensure global compatibility.
What Is the Difference Between IEC and ISO?
The difference lies in the fact that the IEC focuses primarily on electrical and electronic issues, including standards for switchgear and busbar systems such as IEC 61439 temperature rise limits busbars copper current density specifications. In contrast, ISO deals with mechanics and other industrial areas that are less specific to electrical components.
What Benefits Does Compliance with Standards for Switchgear and Busbar Systems Offer Companies?
Compliance with standards for switchgear and busbar systems not only promotes safety and compliance but also allows companies to achieve higher efficiency through optimized production processes and reduced downtime. Standards provide a unified foundation that enables companies to better utilize resources and implement innovations more quickly.
How Do Standards for Switchgear and Busbar Systems Contribute to Innovation?
They provide a framework that enables companies to develop technological solutions safely and drive innovation. By adhering to proven standards, new products can be brought to market more quickly without compromising safety or quality. This helps companies develop new advanced technologies and introduce new business models. The UL 489i harmonization with IEC initiative, for example, enables manufacturers to develop next-generation circuit breakers that serve global markets efficiently.
How Do the IEC 61439 Temperature Rise Limits Impact Busbar Design?
The IEC 61439 temperature rise limits directly influence busbar sizing and material selection. Engineers must ensure that the current density copper busbarvalues result in temperature rises within permissible limits under worst-case operating conditions. The IEC 61439 busbar current carrying capacity table copper 415V provides specific derating factors that account for ambient temperature, ventilation, and enclosure type, ensuring that installations remain within safe operating temperatures throughout their service life.
What is the Significance of UL 489i IEC Harmonization?
The UL 489i IEC harmonization represents a significant milestone in global standardization efforts. By aligning testing requirements and performance criteria between UL and IEC standards for molded-case circuit breakers, this harmonization reduces the burden on manufacturers serving international markets.