What is a Busbar Fabrication Machine?
A busbar fabrication machine is industrial equipment engineered to process copper and aluminum busbars through three primary operations: cutting to precise lengths, punching holes and slots for mounting hardware, and bending to complex angles for fitting within electrical enclosures. These busbar machines are essential for manufacturing electrical distribution systems, switchgear assemblies, and control panels across industrial, commercial, and utility applications.
The evolution from manual processing to CNC busbar machines has transformed busbar production, enabling manufacturers to achieve tighter tolerances, faster throughput, and reduced material waste. Modern copper busbar machines integrate servo-driven positioning, hydraulic power systems, and intelligent nesting software to optimize every aspect of bus bar fabrication.
Types of Busbar Processing Machines
In the following, we will introduce the different types of machines available for busbar production.
Portable 3-in-1 Busbar Machines
The 3-in-1 busbar machine combines cutting, punching, and bending functions in a compact, mobile unit ideal for field installation work and small-batch production. These portable hydraulic busbar bending machines typically handle copper bars up to 12×120 mm, making them perfect for maintenance teams and electrical contractors. Key advantages include low initial investment, quick setup without extensive training, and mobility for on-site fabrication.
Portable 3-in-1 busbar machine offering mobility and versatility for field operations
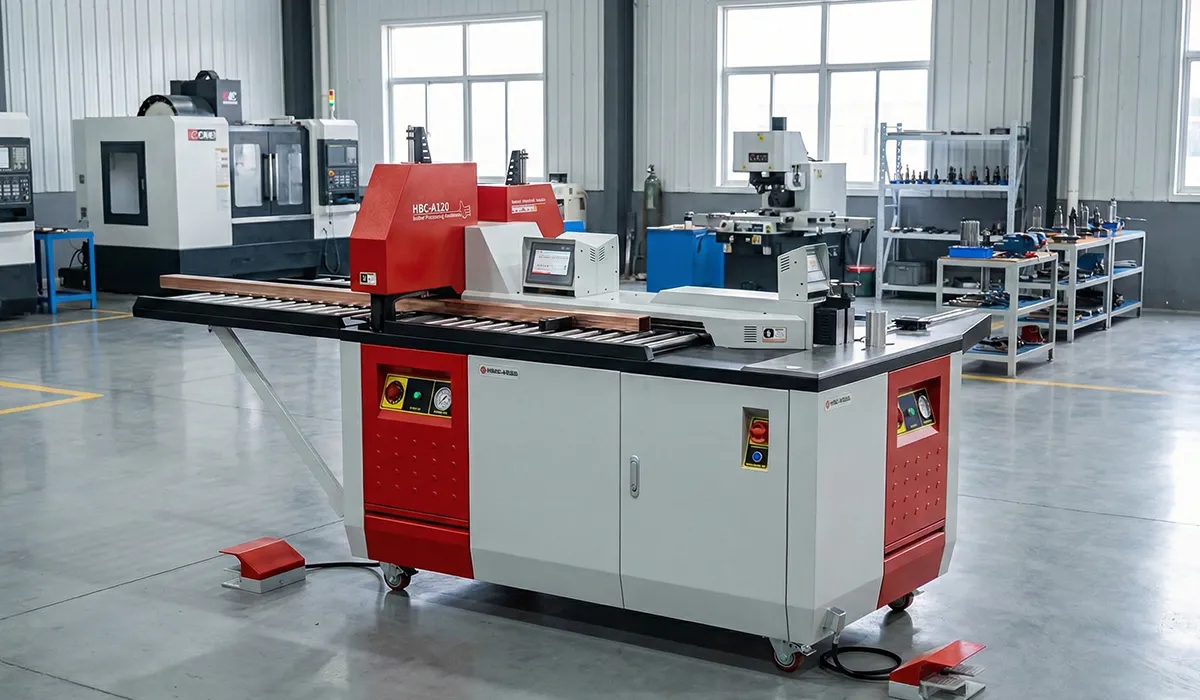

CNC Busbar Punching Machines
CNC busbar punching machines provide automated hole and slot creation with programmable positioning accuracy. These specialized busbar punching machines use servo-controlled X-Y tables to position bars precisely, while hydraulic punches deliver consistent force for clean holes. Modern hydraulic busbar punching machines can handle dies from M6 to M20 and achieve positioning repeatability within ±0.02 mm, critical for high-voltage switchgear applications.
For more information and to get better acquainted, you can visit the product of Punching Machines.
CNC Busbar Bending Machines
Dedicated CNC busbar bending machines excel at repetitive angle work with exceptional consistency. Unlike manual benders, these copper busbar bending machines use angle feedback sensors and servo-hydraulic control to maintain ±0.3° accuracy across thousands of bends. The aluminum busbar bending machine variant accommodates the different material properties of aluminum alloys, adjusting pressure and speed automatically.
Integrated CNC Busbar Processing Centers
The ultimate busbar fabrication equipment solution is the fully integrated CNC busbar processing machine. These automated centers combine all three operations cutting, punching, and bendingwith computer-controlled sequencing, automatic tool changers, and real-time quality monitoring. Top-tier busbar processing machines from leading busbar machine manufacturers can process bars up to 20×300 mm with minimal operator intervention, ideal for high-mix manufacturing environments.
Busbar Machine Specifications: Key Capacity Comparison
| HBC-CP.CNC200 | MODEL |
|---|---|
| Cutting and punching busbars simultaneously | Function |
| Up to 200 x 15 mm | Cutting capacity |
| Busbar size: 200 x 15 mm | Circle dies: M6 to M20 | Punching capacity |
| CNC controller with servo positioning | Puncher center finder |
| Ball Screw and Servo Motors | Length measuring system |
| One Power Pack, Double Acting System | Hydraulic system |
| 400 KN (40 tons) | Max Force |
| 200 Bar | Operating pressure |
| 1 x 11 kW | Power rating |
| 380 Volt – 3 Phase / 50 Hz | Voltage |
| Hydraulic oil H68 – 290 liters | Oil specification |
| 537 x 240 x 188 cm (L x W x H) | Main desk dimensions |
Selecting the Right Busbar Processing Machine
Choosing between busbar fabrication equipment options requires careful analysis of your current and future production needs. Start by documenting your maximum copper busbar dimensionsboth thickness and width—across all current projects. Project your requirements 3-5 years forward, accounting for potential upgrades in electrical distribution capacity or new markets requiring larger conductors.
If the information related to Selecting the Right Busbar was interesting and informative to you, researching topic Y can be very engaging.
Selection Criteria for Busbar Machines:
- Material capacity: Verify maximum thickness × width for copper and aluminum bars
- Hole patterns: Confirm die sizes (M6-M20+) match your mounting hardware specifications
- Bending angles: Ensure the machine handles your required bend types (flat, edge, offset, twist)
- Accuracy requirements: Match machine tolerances to your design specifications
- Production volume: Calculate cycle times against your daily/weekly output targets
- Footprint & power: Confirm the machine fits your facility and electrical service
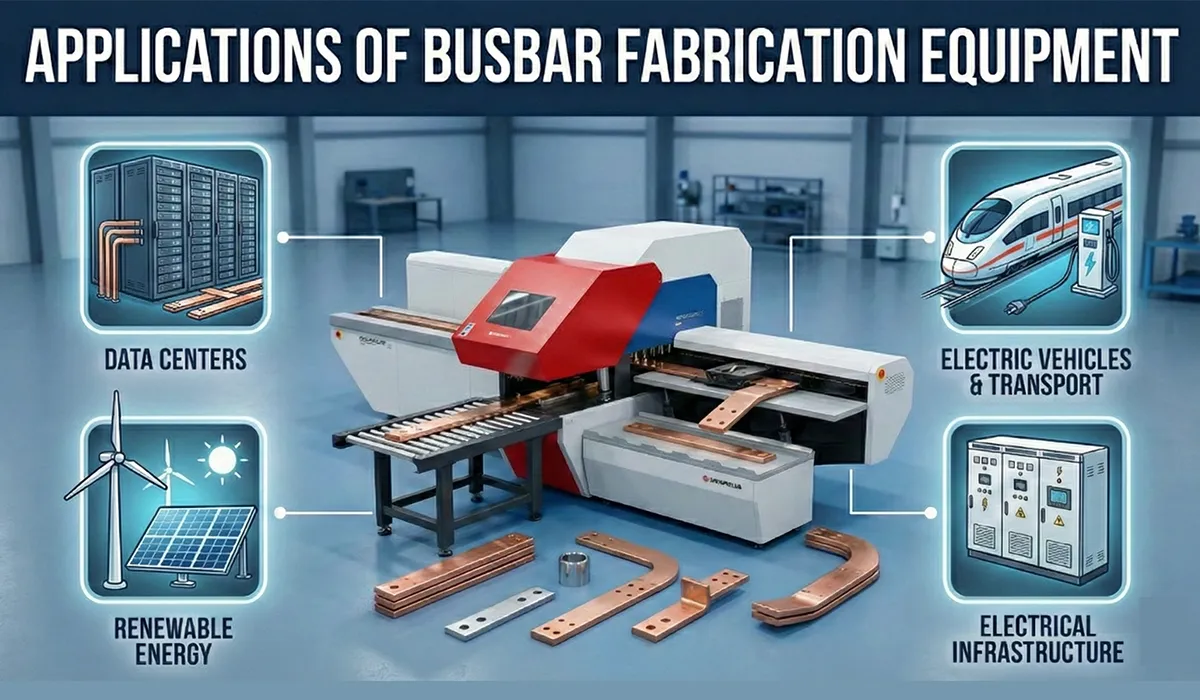
Applications of Busbar Fabrication Equipment
Busbar processing machines serve diverse applications across electrical infrastructure. In switchgear manufacturing, CNC busbar punching machines create precise mounting holes for circuit breakers and disconnect switches. Control panel builders rely on busbar bending and punching machines to fabricate custom distribution blocks that fit compact enclosures. Power distribution companies use heavy-duty copper bar punching machines for substation busbars handling thousands of amperes.
The renewable energy sector increasingly depends on automatic busbar processing machines for solar inverter assemblies and battery energy storage systems. Data centers require specialized copper busbar fabrication for high-current power distribution units (PDUs). Electric vehicle charging infrastructure manufacturers use portable busbar machines for field installation of charging stations.
If the information on topic Applications of Busbar Fabrication was engaging and informative for you, gathering more knowledge about topic Aluminum Busbar could be very exciting.
| Machine Type | Capacity (T × W) | Accuracy | Best Applications | Investment Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Portable 3-in-1 System | Up to 12 × 120 mm | Manual gauges | Field work, small batches, maintenance | Low |
| Professional Bending Machine | 3-20 × 15-160 mm | CNC ±0.3° | Repetitive bends, medium production | Medium |
| CNC Punching Center | 15 × 200 mm | ±0.02 mm positioning | Complex hole patterns, automation | Medium-High |
| Integrated Processing Center | 15-20 × 160-300 mm | ±0.3° / ±0.02 mm | High-mix manufacturing, full automation | High |
Leading Busbar Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers
The global market for busbar fabrication machines includes specialized manufacturers offering equipment from entry-level hydraulic systems to sophisticated CNC processing centers. When evaluating busbar processing machines suppliers, consider factors beyond price: local service support, spare parts availability, operator training programs, and software updates. Established busbar machine manufacturers typically provide factory acceptance testing (FAT) where you can validate performance on your actual parts before shipment.
Request demonstrations of critical features like the CNC busbar punching machine positioning accuracy, hydraulic pressure consistency, and software interface usability. For copper busbar processing machines, verify that tooling packages include dies for your specific hole patterns and that blade materials suit your production volume. Many busbar fabrication machine suppliers offer application engineering support to optimize your process parameters.
If the details you gathered about Busbar Machine Manufacturerswere interesting and insightful, you may find diving deeper into Busbar Bending Techniques equally captivating.
Standards & Compliance for Busbar Production
Professional busbar fabrication must comply with industry standards governing materials, processing, and final assembly. ASTM B187 specifies requirements for copper bus bar material, defining composition, electrical conductivity, and dimensional tolerances. EN 13601:2021 provides European standards for copper rod, bar, and wire used in electrical applications, including mechanical properties and surface quality.
For switchgear assemblies, IEC 61439 establishes design verification and routine testing requirements. North American projects typically reference UL 508A for industrial control panels and UL 857 for busway systems rated up to 600V and 6000A. When specifying busbar processing equipment, ensure your machine capabilities align with the tolerances and documentation requirements of these standards.
Conclusion
Selecting the right busbar fabrication machine shapes your shop’s capabilities for years to come. Whether you choose a versatile 3-in-1 busbar machine for field flexibility, a specialized CNC busbar punching machine for hole accuracy, or a comprehensive CNC busbar processing center for automated production, match the equipment to your current workload and 3-5 year growth trajectory. Prioritize machines from established busbar machine manufacturers offering local service support, comprehensive training, and documented compliance with ASTM, IEC, and UL standards relevant to your markets.
The evolution toward automatic busbar processing machines with intelligent controls and Industry 4.0 connectivity continues to accelerate. Invest in equipment that supports your quality goals today while providing the automation pathway for tomorrow’s competitive landscape. Validate every claim through factory acceptance testing on your actual parts—the best busbar fabrication equipment proves its value in real-world production, not just on specification sheets.
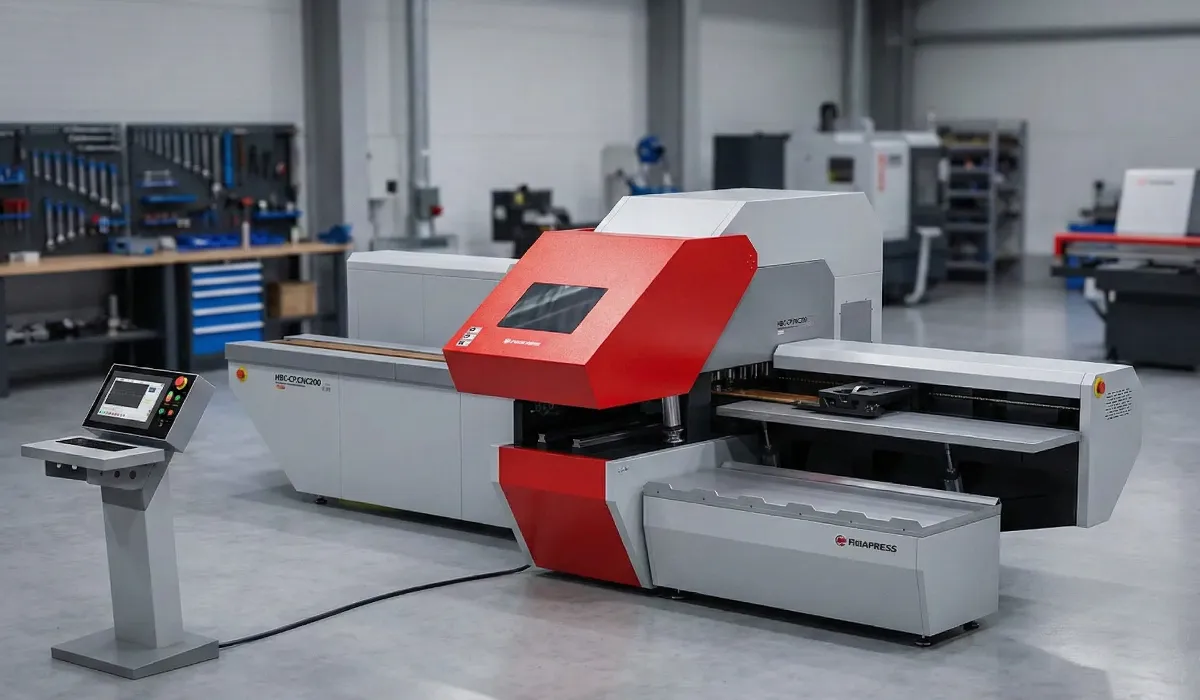









Payapress fabrication machines look very practical for modern industrial production. They seem to improve precision, speed, and overall workflow efficiency in fabrication processes.