Market Insight: The global supercapacitor market is projected to reach $8.3 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 20.8% (Markets and Markets, 2025). This explosive growth is driven by increasing demand for rapid energy storage in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and industrial electrical panels.
As industries experience rapid growth, the need for efficient and sustainable energy storage has become increasingly critical. Supercapacitors, as an innovative technology in energy storage, have revolutionized various sectors with their unique characteristics. These advanced capacitors, capable of delivering high power and ultra-fast charging, offer an attractive solution to energy challenges in industrial electricity and power systems.
From managing peak consumption in manufacturing facilities to supporting renewable energy systems, supercapacitors play a pivotal role. But why are supercapacitors an enticing alternative to traditional batteries? Ultra-fast charging speed, exceptional lifespan, and superior safety are just some of the answers. However, this technology is not without its challenges.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the applications, advantages, technical specifications, and challenges of supercapacitors to give you a better understanding of their potential in transforming the electrical industry.
What is a Supercapacitor? Understanding the Technology
A supercapacitor, also known as an ultracapacitor or electric double-layer capacitor (EDLC), is an advanced energy storage device that offers unique features compared to traditional capacitors and batteries. In simple terms, a supercapacitor is a type of capacitor that can store and release a large amount of electrical energy in a very short period.
Unlike regular capacitors that have limited capacity, supercapacitors can store energy on a much larger scale due to their high energy density and unique design. While conventional capacitors store energy in the range of microfarads to millifarads, supercapacitors can achieve capacitances ranging from 1 farad to over 5,000 farads.
If the information related to topic Supercapacitor was interesting and informative to you, researching topic All Types of Electrical Panels can be very engaging.
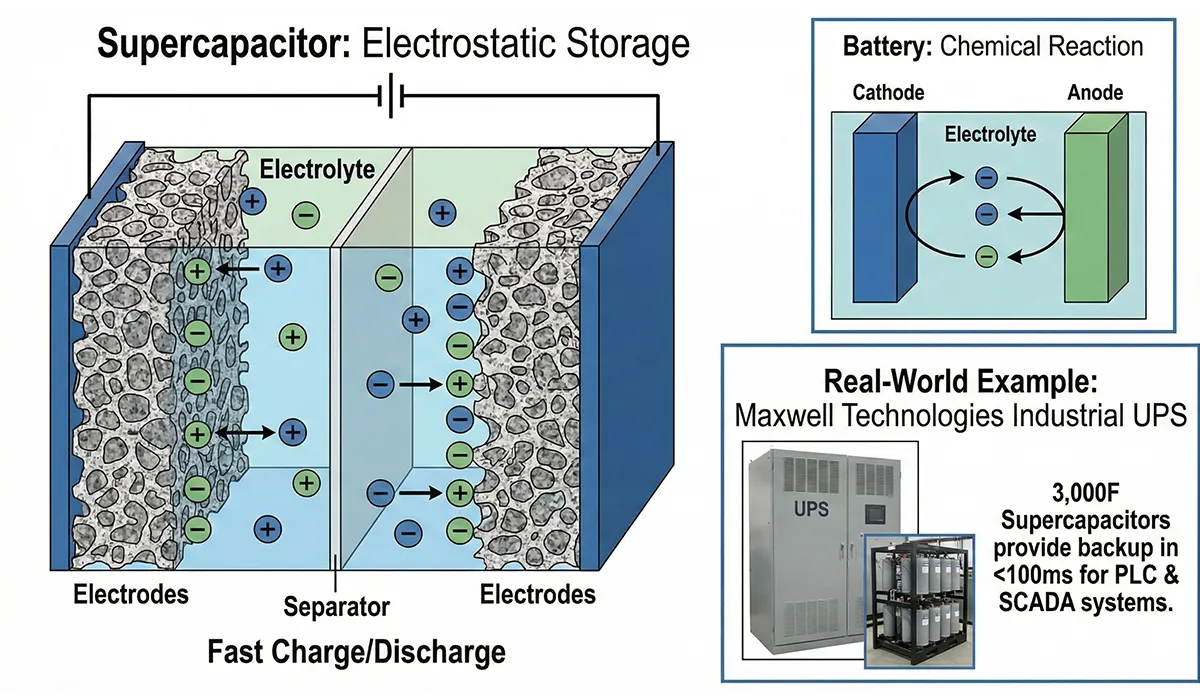
How Do Supercapacitors Work?
Supercapacitors store energy electrostatically on the surface of porous electrodes, unlike batteries which store energy through chemical reactions. This fundamental difference enables supercapacitors to charge and discharge much faster than batteries.
Real-World Example: In Maxwell Technologies’ industrial UPS systems, 3,000-farad supercapacitors can provide backup power in less than 100 milliseconds, protecting sensitive PLC and SCADA systems from even the briefest power interruptions—something traditional battery systems cannot achieve.
Internal Structure of a Supercapacitor
Imagine a supercapacitor as an “electrical sandwich” consisting of:
- Two porous electrodes (typically made of activated carbon with extremely high surface area—up to 2,000 m²/g)
- Electrolyte layer (liquid or solid) separating the electrodes
- Separator membrane preventing short-circuits while allowing ion flow
- Current collectors (usually aluminum or copper foils) for electrical connection
This structure creates an electric double layer at the electrode-electrolyte interface, where charge separation occurs. The extremely high surface area of the porous electrodes allows for massive charge storage—the key to supercapacitors’ high capacitance.
Further exploration of Supercapacitors can be found in the following recommended reading.
Types of Supercapacitors: A Detailed Comparison
Supercapacitors are divided into three main categories, each optimized for specific applications:
1. Electric Double-Layer Capacitors (EDLC)
The most common type, utilizing carbon-based materials with extremely high surface area, such as activated carbon, carbon nanotubes, or graphene. EDLCs store charge purely through electrostatic means without chemical reactions.
Key Characteristics:
- Capacitance: 1-5,000 farads per cell
- Energy density: 5-10 Wh/kg
- Power density: 10,000+ W/kg
- Cycle life: 1,000,000+ cycles
- Applications: UPS systems, voltage stabilization, consumer electronics
Real-World Example: Skeleton Technologies produces curved graphene EDLCs with energy densities up to 11 Wh/kg and power densities exceeding 20,000 W/kg, used in Formula E racing cars for regenerative braking systems.
2. Pseudocapacitors
These capacitors use fast surface chemical reactions (Faradaic processes) to increase capacity. They employ materials like metal oxides (RuO₂, MnO₂), conducting polymers, or transition metal compounds.
Key Characteristics:
- Capacitance: 100-15,000 farads per cell
- Energy density: 10-30 Wh/kg
- Power density: 5,000-10,000 W/kg
- Cycle life: 100,000-500,000 cycles
- Applications: Hybrid vehicles, medical devices, power tools
Real-World Example: CAP-XX manufactures thin-film pseudocapacitors using proprietary polymer materials, achieving energy densities of 25 Wh/kgideal for pulsed power applications in telecommunications equipment.
3. Hybrid Supercapacitors
A combination of EDLC and pseudocapacitor technologies, or battery-capacitor hybrids (lithium-ion capacitors), designed to achieve a balance between energy density and power density.
Key Characteristics:
- Capacitance: Variable (500-10,000 farads)
- Energy density: 15-40 Wh/kg
- Power density: 8,000-15,000 W/kg
- Cycle life: 500,000+ cycles
- Applications: Renewable energy storage, electric buses, grid stabilization
Real-World Example: Japanese Shinkansen high-speed trains use hybrid supercapacitors from JM Energy to capture regenerative braking energy—each train car is equipped with a 50 kW hybrid system that recovers up to 30% of braking energy.
This article serves as a valuable resource for those seeking detailed information on Types of Supercapacitors.
| Specification | EDLC | Pseudocapacitor | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density (Wh/kg) | 5-10 | 10-30 | 15-40 |
| Power Density (W/kg) | 10,000+ | 5,000-10,000 | 8,000-15,000 |
| Cycle Life | 1,000,000+ | 100,000-500,000 | 500,000+ |
| Charge Time | 1-10 seconds | 10-60 seconds | 10-30 seconds |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +70°C | -20°C to +60°C | -30°C to +65°C |
| Cost (Relative) | Medium | High | Medium-High |
| Primary Applications | UPS, Consumer Electronics | EVs, Medical Devices | Renewable Energy, Transit |
| Self-Discharge Rate | 10-40% per month | 5-20% per month | 3-15% per month |
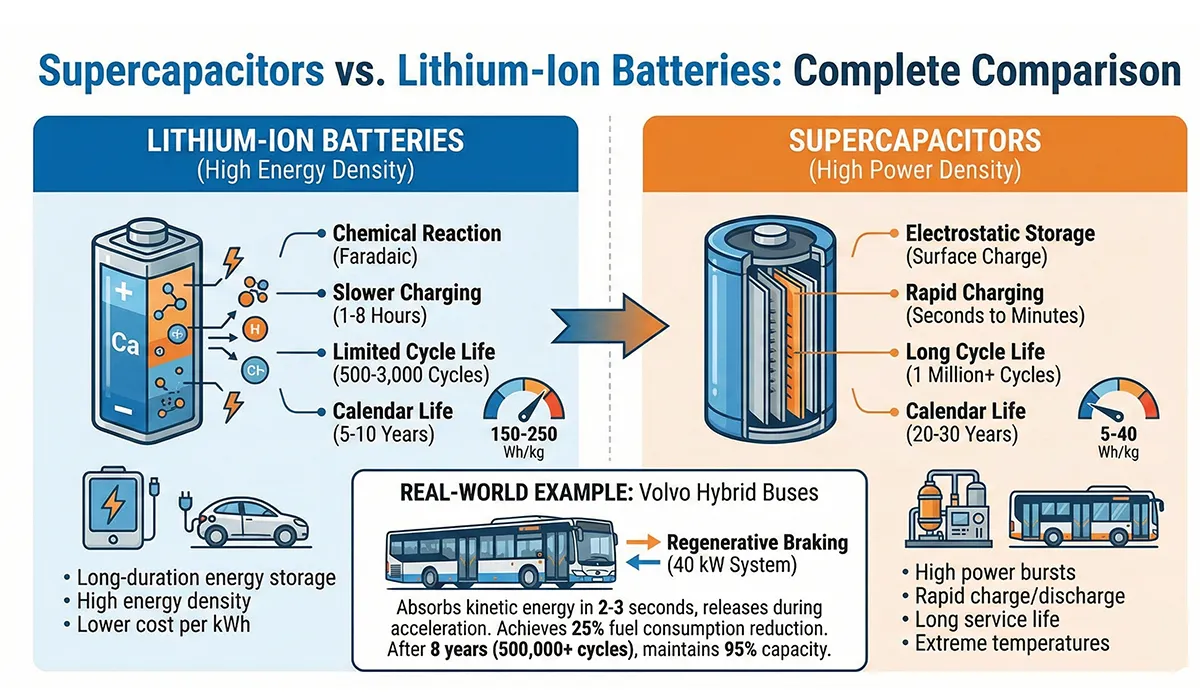
Supercapacitors vs Lithium-Ion Batteries: Complete Comparison
The key difference between supercapacitors and batteries lies in how they store energy and their performance characteristics.
Batteries, especially lithium-ion batteries, have higher energy density (150 to 250 watt-hours per kilogram) and can store more energy for a given volume and weight. In contrast, supercapacitors have lower energy density (5 to 40 watt-hours per kilogram depending on type) but offer significantly higher power density, meaning they can release or absorb large amounts of energy in very short time periods.
If the information about topic Lithium-Ion Batteries was valuable and interesting to you, researching topic Rittal Electrical Panels could be just as captivating.
Storage Mechanism Differences:
- Batteries: Store energy through chemical reactions (Faradaic processes) involving ion intercalation into electrode materials. This is slower but allows higher energy density.
- Supercapacitors: Store energy electrostatically by holding electric charge on electrode surfaces. This is much faster but provides lower energy density.
Charging and Lifespan:
- Charging Speed: Supercapacitors can be charged or discharged in seconds to minutes, whereas fully charging a lithium-ion battery typically takes 1-8 hours. This makes supercapacitors invaluable for energy recovery systems like regenerative braking.
- Cycle Life: Supercapacitors can withstand up to 1 million charge/discharge cycles without significant capacity loss, while lithium-ion batteries typically have a limited lifespan of 500 to 3,000 cycles. This makes supercapacitors ideal for applications requiring frequent charging and discharging.
- Calendar Life: Supercapacitors can last 20-30 years in industrial applications, while lithium batteries typically degrade after 5-10 years even with minimal use.
Real-World Example: Volvo’s hybrid buses in Gothenburg, Sweden utilize 40 kW supercapacitor systems for regenerative braking. During each stop, the system absorbs kinetic energy in 2-3 seconds and releases it during acceleration, achieving 25% fuel consumption reduction. After 8 years of operation (over 500,000 brake cycles), the supercapacitors maintain 95% of their original capacity—while equivalent lithium batteries would have required 3-4 replacements.
When to Use Supercapacitors vs Batteries:
Choose Supercapacitors for:
• High power bursts (starting motors, pulse loads)
• Rapid charge/discharge cycles (regenerative braking)
• Long service life requirements (industrial equipment)
• Extreme temperature environments (-40°C to +70°C)
• High reliability/safety critical applications
Choose Batteries for:
• Long-duration energy storage (hours to days)
• High energy density requirements (portable devices)
• Lower cost per kWh stored
• Gradual discharge applications
| Parameter | Supercapacitor | Lithium-Ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 5-40 Wh/kg | 150-250 Wh/kg |
| Power Density | 5,000-20,000 W/kg | 500-2,000 W/kg |
| Charge Time | 1-30 seconds | 1-8 hours |
| Discharge Time | Seconds to minutes | Minutes to hours |
| Cycle Life | 500,000 – 1,000,000+ | 500 – 3,000 |
| Calendar Life | 20-30 years | 5-10 years |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +70°C | -20°C to +60°C |
| Safety | Very High (no explosion risk) | Moderate (thermal runaway risk) |
| Efficiency | 95-98% | 85-95% |
| Self-Discharge | 10-40% per month | 2-5% per month |
| Cost per kWh | $10,000 – $30,000 | $100 – $300 |
| Environmental Impact | Lower (carbon-based, recyclable) | Higher (mining, disposal challenges) |
| Maintenance | None required | Battery management system needed |
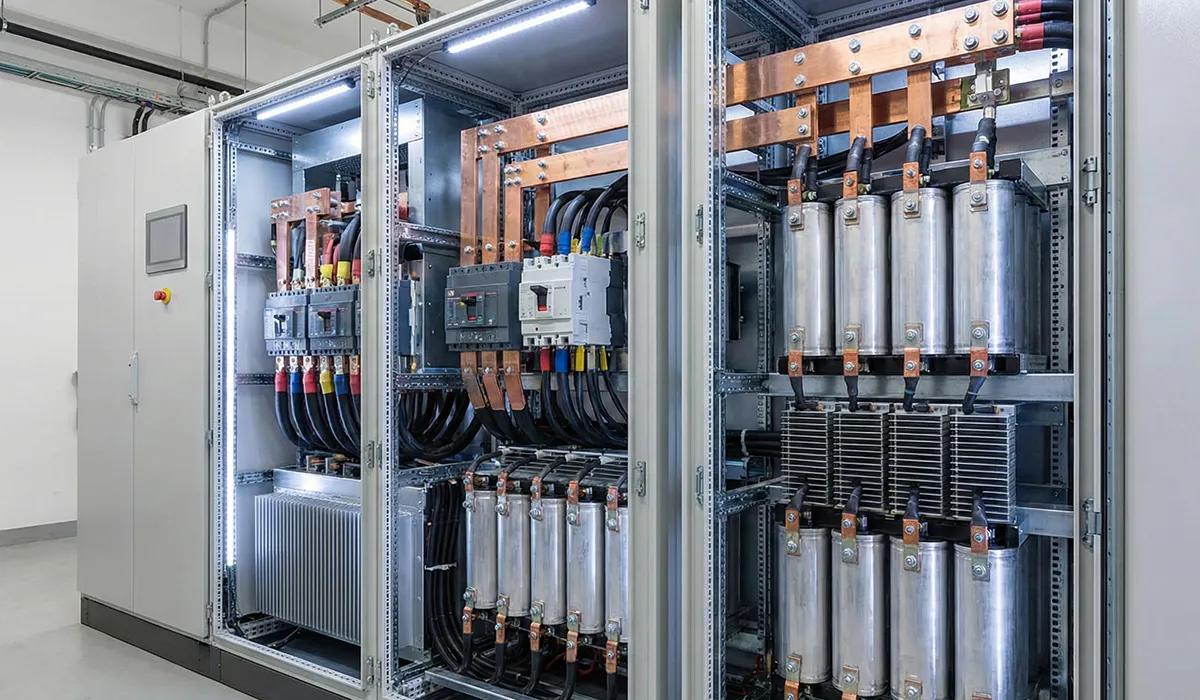
Industrial Electrical Panel Applications: Why Contractors Need Supercapacitors
In industrial electrical systems, supercapacitors play a vital role in improving stability, reliability, and efficiency. Here’s why electrical contractors and facility managers are increasingly specifying supercapacitors in electrical panel designs:
1. UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) Systems
Supercapacitors can supply energy in a fraction of a second to prevent power outages and protect sensitive equipment. Unlike battery-based UPS systems that take 20-50 milliseconds to activate, supercapacitor UPS systems respond in under 5 milliseconds.
Real-World Example: At Intel’s Fab 32 facility in Arizona, supercapacitor-based UPS systems protect semiconductor manufacturing equipment worth millions. A single power disruption can ruin entire wafer batches—the <5ms response time of supercapacitors prevents this, whereas traditional battery UPS systems were too slow.
Technical Specifications for Industrial UPS:
- Typical capacitance: 500-3,000 farads per module
- Voltage range: 48V DC to 400V DC
- Backup time: 10-60 seconds (bridging time until generators start)
- Response time: < 5 milliseconds
- Service life: 15-20 years without replacement
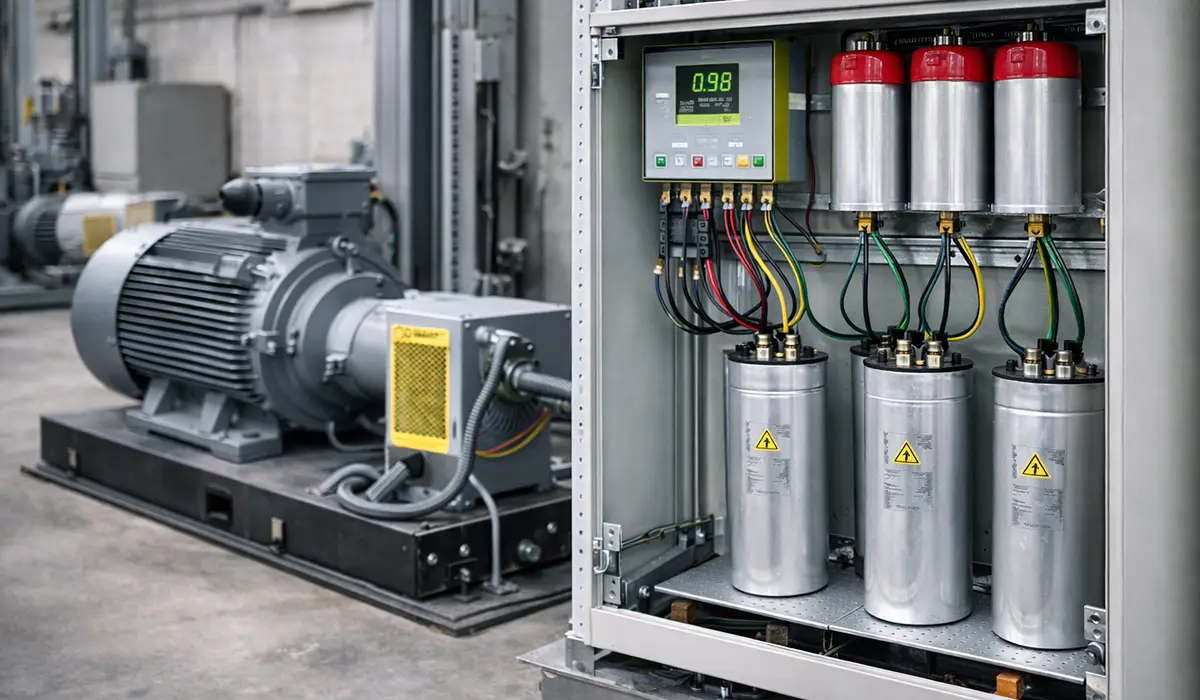
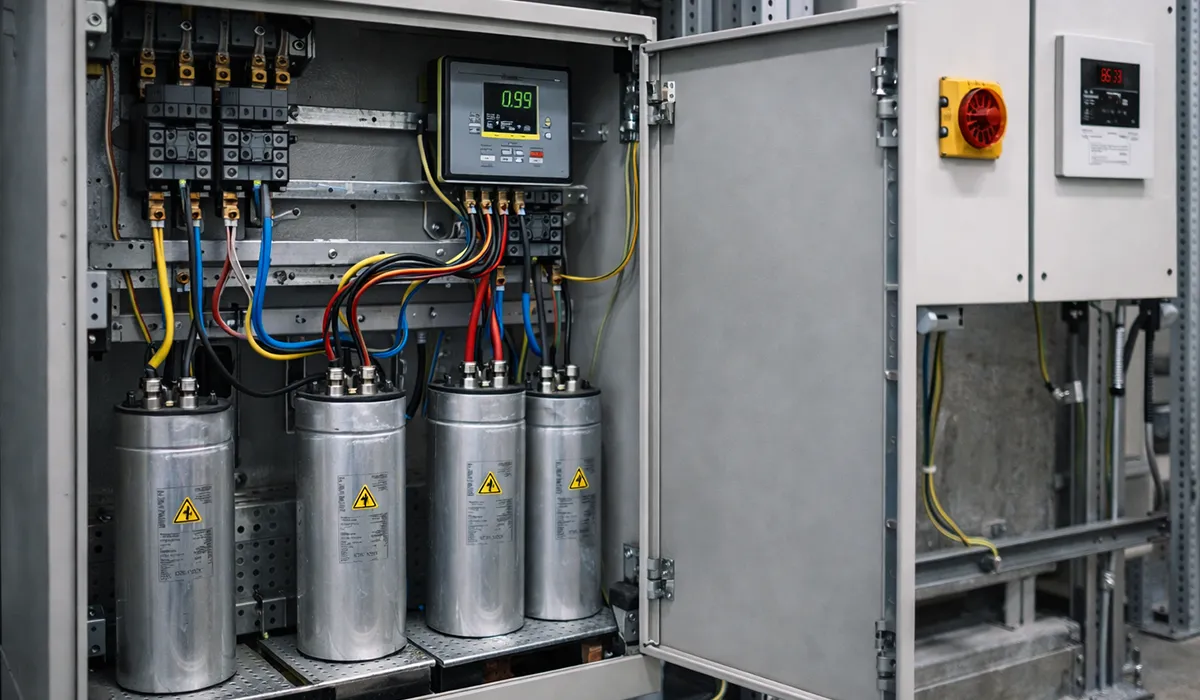
2. Voltage Stabilization and Power Quality
In stabilizers and power conditioning equipment, supercapacitors control fluctuations and stabilize voltage during transient events, motor starting, or sudden load changes.
Real-World Example: Siemens incorporates supercapacitor banks in their SITOP industrial power supplies to handle voltage sags and swells in harsh industrial environments, maintaining stable output voltage within ±1% even during severe grid disturbances.
3. Peak Power Management and Demand Charge Reduction
A standout application is peak consumption management in factories and power grids. By storing energy during off-peak hours and releasing it during peak demand, supercapacitors reduce energy costs and relieve pressure on the grid.
Financial Impact: Industrial facilities can save 15-30% on electricity costs by reducing demand charges. For a medium-sized manufacturing plant paying $50,000/month, this translates to $7,500-$15,000 monthly savings.
Real-World Example: AES Energy Storage deployed a 2 MW supercapacitor system at a California manufacturing facility, shaving peak demand by 400 kW and saving the plant $180,000 annually in demand charges.
Why Electrical Contractors Need Supercapacitors in Control Panels:
1. Reduce Maintenance Costs by 30-40%
• 10x longer lifespan than batteries (20 years vs 2-5 years)
• No battery replacement labor or disposal costs
• Zero maintenance requirements
2. Prevent Million-Dollar Losses
• In sensitive industries (data centers, petrochemical, hospitals), every second of downtime can cost thousands
• <5ms response time prevents equipment damage and production losses
• Critical for PLC, SCADA, and process control systems
3. Increase System Reliability
• Stable operation from -40°C to +70°C (battery UPS limited to -20°C to +40°C)
• No degradation in extreme temperatures
• 98% round-trip efficiency vs 85-90% for batteries
4. Save Panel Space
• 50% smaller footprint than equivalent battery systems
• Lighter weight (important for wall-mounted panels)
• Can be mounted in any orientation
5. Meet Modern Codes and Standards
• UL 810 certified supercapacitors available
• No special ventilation requirements (unlike battery rooms)
• Safer chemistry—no thermal runaway or explosion risk
• Compliant with IEEE 1184 and IEC 61000 standards
| Application in Electrical Panels | Typical Capacitance | Response Time | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| UPS Backup Power | 500-3,000F | < 5ms | Equipment Protection |
| Voltage Stabilization | 100-500F | < 1ms | Power Quality |
| Motor Starting / Peak Shaving | 1,000-5,000F | 10-100ms | Cost Reduction |
| Regenerative Drive Systems | 200-1,000F | < 10ms | Energy Recovery |
| Grid Frequency Regulation | 2,000-10,000F | < 20ms | Grid Stability |
Electric and Hybrid Vehicle Applications
The primary use of supercapacitors in transportation is in regenerative braking systems. When a vehicle brakes, kinetic energy is converted to electrical energy, which supercapacitors can quickly absorb and store. This energy is then reused during acceleration, increasing the overall efficiency of the vehicle.
For a comprehensive understanding of Hybrid Vehicle, we highly recommend reviewing this article.
Why Supercapacitors Excel in Automotive Applications:
- High peak power: Can deliver 10-20 kW for acceleration boost in hybrid vehicles
- Cold weather performance: Unlike lithium batteries, supercapacitors maintain full performance at -40°C
- Extended battery life: Reducing peak loads on batteries extends their service life by 40-60%
- Fast energy capture: Can absorb 80-90% of regenerative braking energy vs 40-60% for batteries alone
Real-World Examples:
- Toyota TS050 Hybrid (Le Mans Racing): Uses an 8 megajoule supercapacitor system providing up to 500 horsepower boost for 6-8 seconds—crucial for overtaking and corner exit acceleration.
- PSA Peugeot Citroën Hybrid Air: Production vehicles use supercapacitors to store braking energy, achieving fuel consumption of just 2.9 L/100km in city driving.
- Mazda i-ELOOP System: World’s first production capacitor-based regenerative braking system, using a 25-farad electric double-layer capacitor that fully charges in seconds and powers accessories, reducing alternator load and saving 10% fuel.
- BYD Electric Buses: Combine supercapacitors with lithium batteries—supercapacitors handle regenerative braking and acceleration bursts, while batteries provide range. This extends battery life from 3 years to 8+ years.
| Vehicle Type | Supercapacitor Application | System Capacity | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hybrid Cars | Regenerative braking, power assist | 0.5-2 kWh | 10-15% fuel saving |
| Electric Buses | Fast charging stations, braking recovery | 5-20 kWh | 25-30% energy recovery |
| Rail/Metro | Station braking energy capture | 50-200 kWh | 30-40% energy recovery |
| Racing Vehicles | KERS (Kinetic Energy Recovery) | 2-8 MJ | 500+ HP boost |
| Forklifts/Industrial | Start-stop cycles, lifting | 1-5 kWh | 20-35% efficiency gain |
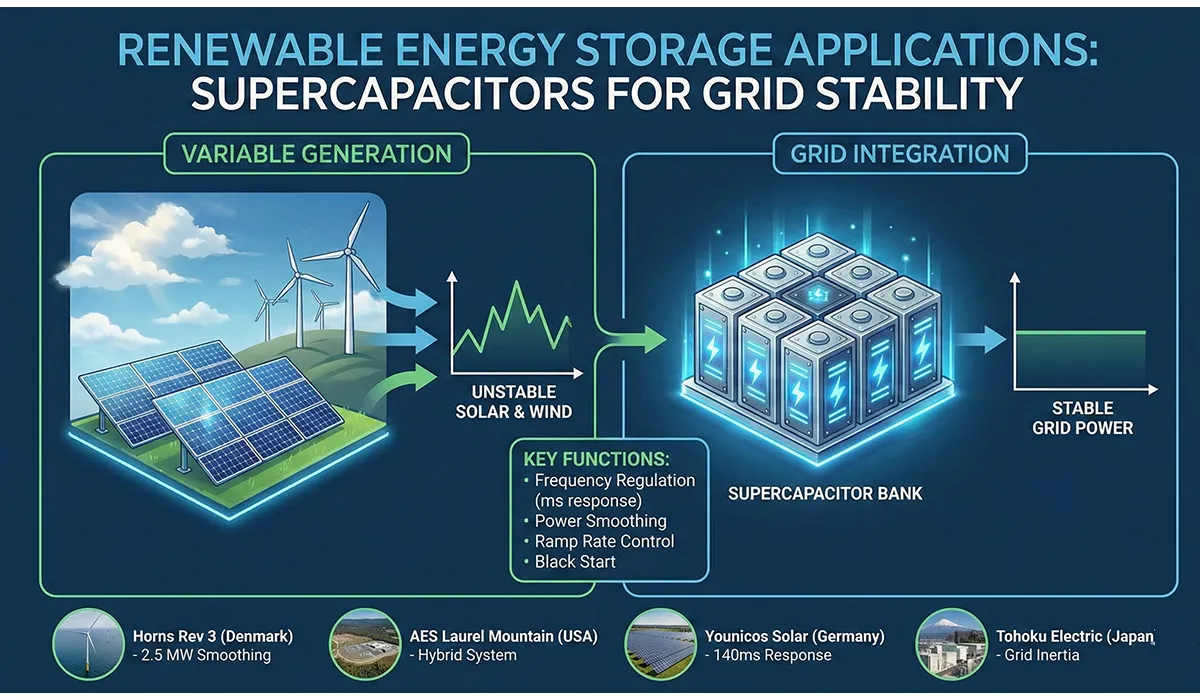
Renewable Energy Storage Applications
In solar and wind energy systems, power production is unstable and variable. Supercapacitors can serve as intermediaries to stabilize fluctuations and provide instant power when needed.
Key Renewable Energy Applications:
- Grid Frequency Regulation: Respond to frequency deviations in milliseconds, much faster than batteries (seconds) or generators (minutes)
- Power Smoothing: Filter out rapid fluctuations in wind/solar output to deliver stable grid power
- Ramp Rate Control: Manage rapid changes in renewable output during cloud cover or wind gusts
- Black Start Capability: Provide initial power to restart grid sections after blackouts
Real-World Examples:
- Horns Rev 3 Wind Farm (Denmark): 2.5 MW supercapacitor bank smooths output fluctuations and maintains grid stability for this 407 MW offshore wind farm.
- AES Laurel Mountain Wind Farm (USA): 98 MW wind farm uses a 32 MW / 8 MWh supercapacitor-battery hybrid system for frequency regulation, responding 10x faster than traditional generators.
- Younicos Solar Farm (Germany): 5 MW supercapacitor system provides rapid response grid services, stabilizing frequency within 140 milliseconds.
- Tohoku Electric Power (Japan): After the 2011 tsunami, implemented supercapacitor systems at multiple substations to provide grid inertia and prevent cascading failures during renewable energy integration.
Technical Advantages in Renewable Energy:
- Can cycle 100,000+ times per year without degradation (batteries limited to 5,000-10,000 cycles/year)
- Operate efficiently in outdoor temperature extremes (-40°C to +70°C)
- Provide both energy storage AND grid services (frequency regulation, voltage support)
- 25-year lifespan matches solar panel warranties
Consumer Electronics Applications
In devices like digital cameras, mobile phones, wearable devices, and flashlights, supercapacitors are used for backup power or fast charging.
Real-World Examples:
- Casio Exilim Camera: Charges in 3 minutes using supercapacitor technology, ready for 160 photos
- Seiko Kinetic Watches: Use micro-supercapacitors that charge from wrist movement and last 6+ months per charge
- LED Flashlights: Brands like NightStar offer supercapacitor flashlights that charge in 90 seconds by shaking and provide 20+ minutes of light
- Wireless Sensors / IoT Devices: Energy harvesting sensors use supercapacitors to store solar/RF energy for years of maintenance-free operation
Heavy Industry and Industrial Machinery
In cranes, forklifts, trains, and mining machinery, supercapacitors provide high instantaneous power when starting large motors or lifting heavy loads.
Real-World Examples:
- Shanghai Metro System: 1.2 MWh supercapacitor systems store braking energy and reduce power consumption by 30%, saving over $2 million annually in electricity costs.
- Port Cranes (Rotterdam): Hybrid supercapacitor systems capture energy when lowering containers and release it when lifting—reducing peak power demand by 50% and extending cable/generator life.
- Electric Forklifts: Crown Equipment hybrid forklifts use supercapacitors to handle peak loads during acceleration and lifting, extending battery life by 40% and reducing maintenance.
- Mining Haul Trucks: Komatsu 930E-4SE electric drive mining trucks use supercapacitors to capture energy during downhill runs and assist diesel engines on uphill climbs, cutting fuel consumption by 25%.
For a comprehensive understanding of Renewable Energy Storage, we highly recommend reviewing this article.
Military and Aerospace Applications
In defense industries, supercapacitors supply quick energy for radars, lasers, and communication systems. In spacecraft, they are an ideal choice due to their performance in extreme temperatures and unique conditions.
Real-World Examples:
- Iridium NEXT Satellites: Use supercapacitors for power management in temperature extremes (-100°C to +100°C), where batteries would fail.
- Directed Energy Weapons: Military lasers and electromagnetic railguns require instant multi-megawatt power bursts—only supercapacitors can deliver this.
- UAV (Drone) Systems: Hybrid battery-supercapacitor systems provide extended flight time while handling high-power maneuvers and sensor loads.
- Missile Guidance Systems: Supercapacitors power high-G maneuvers and terminal guidance radars where batteries would be damaged by acceleration forces.
Advantages and Challenges of Supercapacitors
Key Advantages:
- Ultra-Fast Charging: 10-30 seconds compared to 1-8 hours for batteries
- Exceptional Lifespan: Up to 1 million cycles (20-30 years operational life)
- Superior Safety: No explosion or fire risk, no thermal runaway
- Extreme Temperature Performance: -40°C to +70°C operation
- High Instantaneous Power: Up to 10-20x higher than batteries
- Zero Maintenance: No replacement or servicing required
- High Efficiency: 95-98% round-trip efficiency
- Environmentally Friendly: Carbon-based, fully recyclable, no heavy metals
- Predictable Performance: Linear voltage discharge, simple state-of-charge monitoring
Current Challenges:
- Low Energy Density: 10-20x lower than lithium-ion batteries (limits use in long-duration storage)
- High Initial Cost: $10,000-$30,000 per kWh vs $100-$300 for batteries
- Self-Discharge: Higher rate than batteries (10-40% per month vs 2-5%)
- Voltage Management: Requires sophisticated control circuits for voltage balancing
- Limited Energy Storage Duration: Best for seconds to minutes, not hours to days
- Size and Weight: For equivalent energy storage, much larger and heavier than batteries
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis:
While supercapacitors have 100x higher upfront cost per kWh than batteries, the TCO over 20 years often favors supercapacitors for high-cycle applications:
Example: UPS for Data Center (10 kW, 30-second backup)
• Battery System: $5,000 initial + $4,000 replacement every 3 years = $31,000 over 20 years
• Supercapacitor System: $25,000 initial + $0 replacement = $25,000 over 20 years
Plus reduced downtime risk, no disposal costs, and zero maintenance labor.
Future of Supercapacitors: Emerging Technologies
With the development of nanomaterials and hybrid designs, supercapacitors are expected to play an increasingly significant role in the future energy supply chain:
Breakthrough Technologies in Development:
- Graphene Supercapacitors: Energy density 5x higher with 1-second charge times. Skeleton Technologies has already commercialized curved graphene supercapacitors achieving 60 Wh/kg—approaching battery levels.
- Hybrid Battery-Supercapacitor Systems: Combining advantages of both technologies. Nanotechnology-enabled lithium-ion capacitors achieve 40-50 Wh/kg with 100,000+ cycle life.
- Printed Supercapacitors: For smart clothing and IoT devices. Flexible, thin-film supercapacitors can be printed on fabric or plastic substrates.
- Self-Healing Supercapacitors: Using polymer electrolytes that automatically repair micro-damage, extending cycle life to 2+ million cycles.
- Solid-State Supercapacitors: Eliminating liquid electrolytes for higher energy density and improved safety in extreme conditions.
- Asymmetric Supercapacitors: Combining battery-like and capacitor-like electrodes to optimize both energy and power density.
Market Projections:
- Allied Market Research: Global supercapacitor market will grow from $3.2 billion (2024) to $11.5 billion (2032)
- Markets and Markets: CAGR of 20.8% through 2030, driven by EV and renewable energy adoption
- Graphene-based supercapacitors expected to reach mass production by 2027-2028
If you are looking for more information about topic Emerging Technologies, it is recommended not to miss reading this article.
Conclusion: The Future of Energy Storage
Supercapacitors, with their combination of high power, rapid charging, and exceptional lifespan, are transforming various industries from industrial electrical panels to electric vehicles. While they cannot completely replace batteries, they demonstrate clear superiority in applications requiring high instantaneous power and rapid charging.
The combination of supercapacitors with batteries can enhance system efficiency and lifespan, bringing transformation to sectors like transportation, energy storage, and consumer electronics. As nanomaterial technology advances and costs decrease, supercapacitors will become even more prevalent in the global energy infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between supercapacitors and regular capacitors?
Supercapacitors can store much larger amounts of energy than regular capacitors due to their high energy density and specialized design with porous electrodes. While regular capacitors store microfarads to millifarads, supercapacitors achieve 1-5,000 farads—millions of times more capacitance. They also allow for rapid charge/discharge cycles measured in seconds rather than microseconds.
How do supercapacitors work?
Supercapacitors store energy electrostatically on the surfaces of porous electrodes with extremely high surface area (up to 2,000 m²/g). Unlike batteries that use chemical reactions, supercapacitors hold charge through physical separation of ions at the electrode-electrolyte interface. This allows them to charge/discharge much faster than batteries—in seconds versus hours.
What industries use supercapacitors?
Supercapacitors are used across many industries: industrial power systems and electrical panels (UPS, voltage stabilization, peak shaving), electric and hybrid vehicles (regenerative braking), renewable energy (solar/wind power smoothing), consumer electronics (fast-charging devices), heavy machinery (cranes, forklifts, trains), and defense/aerospace (satellites, directed energy weapons, UAVs).
Can supercapacitors replace batteries?
No, supercapacitors cannot replace batteries in all applications due to their lower energy density (5-40 Wh/kg vs 150-250 Wh/kg for lithium-ion). However, they excel in applications requiring high power bursts, rapid charging, or frequent cycling. The best solution is often a hybrid system combining batteries (for energy storage) with supercapacitors (for power delivery).
What is the cost of supercapacitors?
Supercapacitor pricing varies by type, capacity, and brand: Small units (1-10 farads): $5-$50; Medium modules (100-500 farads): $200-$2,000; Large industrial systems (1,000-5,000 farads): $5,000-$50,000. On a per-kWh basis, supercapacitors cost $10,000-$30,000/kWh versus $100-$300/kWh for batteries. However, the total cost of ownership over 20 years can favor supercapacitors in high-cycle applications.
What temperature range can supercapacitors operate in?
Most supercapacitors operate reliably from -40°C to +70°C, significantly wider than lithium-ion batteries (-20°C to +60°C). Some specialized military/aerospace supercapacitors function from -55°C to +85°C. This makes them ideal for outdoor installations, automotive applications, and extreme climate environments where batteries would fail or require expensive temperature management systems.
Are supercapacitors environmentally friendly?
Yes, supercapacitors are more environmentally friendly than batteries: They use carbon-based materials (not heavy metals like lead, cadmium, or cobalt); they’re fully recyclable; they have no toxic electrolytes (unlike some battery chemistries); their 20-30 year lifespan means less frequent replacement and disposal; and they require no special hazardous waste handling. However, manufacturing still has environmental impact, though much less than battery production.








