Getting to Know the Types of Electrical Wires and Cables
Electrical wires and cables are among the most widely used and important pieces of equipment and are an inseparable part of power networks and power electrical circuits. Wires and cables play a major role in our daily life. From home wiring to an MP3 player, they are used everywhere in our lives. These two pieces of equipment have completely different meanings, but they can sometimes be mistaken for each other.
Although both wire and cable are made with a common conductor to carry electric current (copper or aluminum), the fundamental difference is this: a wire is made of a single conductor strand covered with an insulating layer. You can say a wire is a single conductor. A cable, however, is made of two or more insulated conductors that are twisted together.
To understand different types of wires and cables, it helps to know that many parameters are involved in their classification. Here, we review the most important ones:
- Voltage level
- Conductor type and its construction
- Type of insulation and sheath (jacket)
- Type of electrical protection
- Type of mechanical protection
- Type of application
- Number of cores/strands
- Standard
If this article has been helpful to you, we recommend reading the article on topic Wire Suitable for Industrial for more detailed and accurate information
Types of Electrical Wires
A wire consists of two parts: conductor and insulation. The conductor carries electricity to transfer current from one point to another and is usually made of copper or aluminum because these metals conduct current better than most others.
Wires are measured by cross-sectional area (in mm²). For example, wires with a cross-sectional area of 10 or 20 mm² are used in residential applications.
Keep in mind: wires with a larger cross-sectional area can carry more current.
In general, wires can be divided into three main categories:
- Solid wire (single-core)
- Semi-flexible stranded wire
- Flexible stranded wire
Solid Wire
Solid wire, also known as dry wire, is a single conductor protected by a PVC insulation layer and is used in building construction. This type of wire is also used for internal wiring inside panels and power distribution units. Installation under plaster and inside conduit is permitted. Solid wire is used at high frequencies and also has a lower cost. The rated voltage of this type of wire is 300 to 750 volts.
Semi-Flexible Stranded Wire
The structure of semi-flexible stranded wires is similar to solid wires and they are used in similar areas. The difference is that when more flexibility is needed compared to solid wire, this type of wire is used.
If you found this article beneficial, we suggest reading an article on topic Semi-Flexible Wire for more up-to-date and detailed information.
Flexible Stranded Wire
Flexible stranded wire includes many thin conductor strands twisted together and protected by a plastic (PVC) insulation layer. These wires are used in building wiring and wherever high flexibility is required. For the same current, this type of wire has a larger cross-sectional area than solid wire. The rated voltage of flexible stranded wires is 300 to 750 volts, and they are produced in cross-sectional areas from 0.5 to 240 mm².
If this article has assisted you, reading an article focused on topic Solid Wire Cable will offer more extensive information.
Types of Electrical Cables
One or more conductor cores insulated from their surrounding environment are called a cable. The most common metals used as conductors in wires and cables are high-purity copper and aluminum. The voltage on the cable’s insulation surface relative to earth is zero. The voltage on the conductor surface relative to earth is called the phase voltage and is shown as U0. The symbol U indicates the voltage between conductors.
Classification of Cables by Voltage Level
| Class | Abbreviation | Voltage level |
|---|---|---|
| Low Voltage Cables | LV | 300 to 1000 volts |
| Medium Voltage Cables | MV | 1 to 33 kV |
| High Voltage Cables | HV | 63 to 230 kV |
| Extra High Voltage Cables | EHV | 400 kV and above |
Low-voltage cables include low-voltage power cables and control and instrumentation cables.
Classification of Cables by Conductor Type
Typically, high-purity copper or aluminum is used as the cable conductor due to higher conductivity compared to other metals.
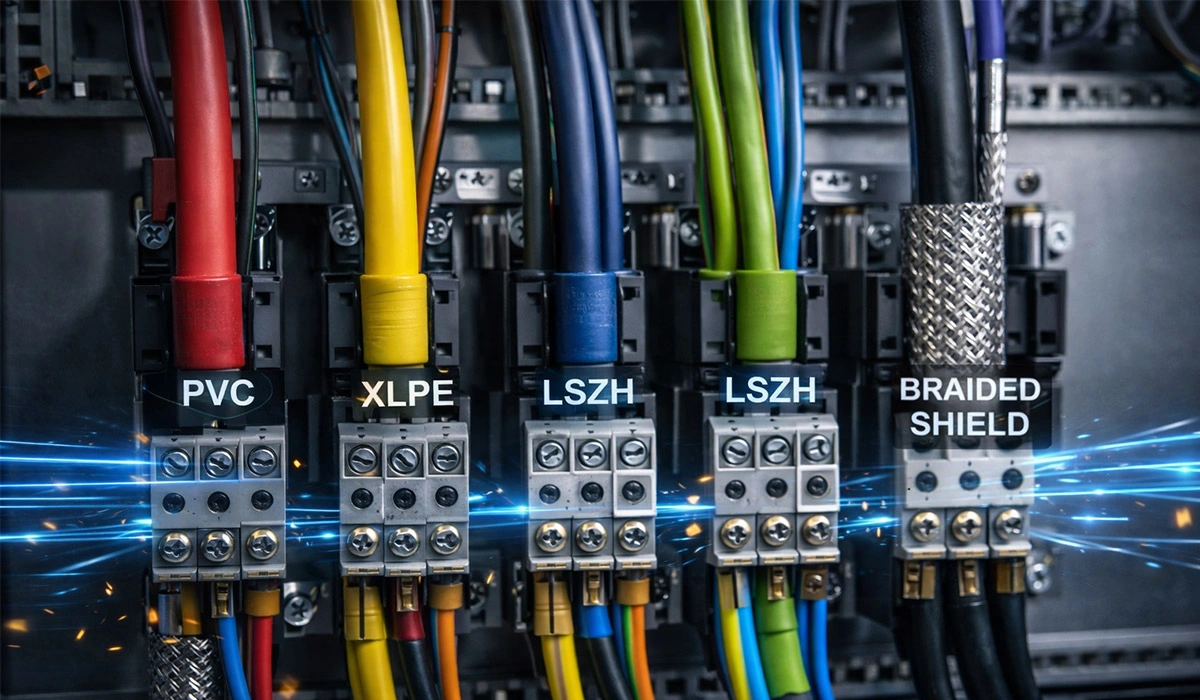

Classification of Cables by Insulation Type
Cable insulation materials include: PVC (polyvinyl chloride), polyethylene (PE), XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene), polyurethane, polyester copolymers, PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), PET (polyethylene terephthalate), NR (natural rubber), EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate), SIR (silicone rubber), and CR (chloroprene rubber).
Classification of Cables by Electrical Protection
In power plants or household meters, to increase electrical protection against noise, a layer of tape or a braided shield made of copper or aluminum is used around the cable.
Classification of Cables by Mechanical Protection
To protect cables against mechanical impact, cuts, and similar damage, various types of metal armoring are used around the cable.
Classification of Cables by Number of Cores
Low-voltage cables (LV) are usually produced with one to five cores, and medium-voltage (ML) as well as high-voltage (HV) cables are produced with one to three cores.
Classification of Cables by Application Type
Underground Cable
One type of electrical cable is the underground cable. It is designed for use in indoor environments and fixed locations. This cable must not be used in places where cable movement is high. It is used to supply energy under soil, in water, in channels, for distribution networks in electrical installations, and wherever mechanical impact is unlikely.
If this content has been beneficial, we recommend reading the article on topic Underground Electrical Conduit for more details and precision.
Telecommunication Cable
Made of several twisted pairs of wires. Twisting prevents noise produced by magnetic coupling. It is used for signal transmission in communications and telecommunications.
Flexible Cable
Consists of one or more conductors insulated from each other and protected by an insulating sheath. It is used for control and connection in machines, conveyor belts, production lines, machine tool industries, advanced assembly lines, automatic equipment, and for medium mechanical stress, provided it is not in direct contact with heat.
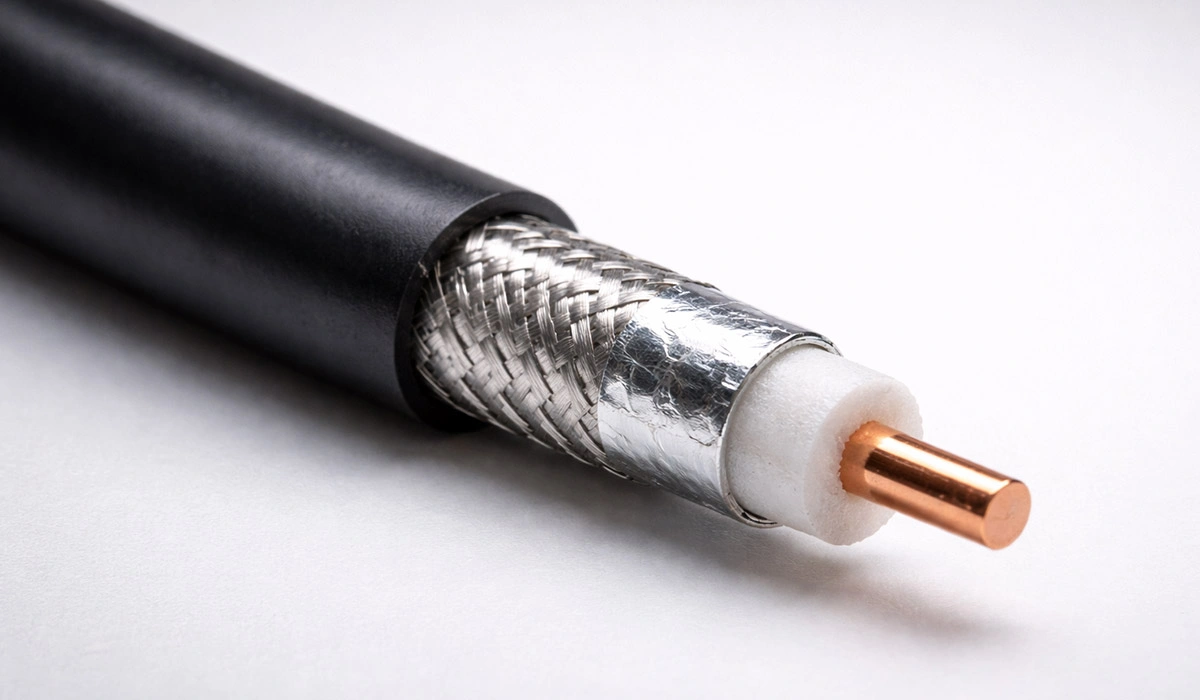

Coaxial Cable
Has an internal conductor surrounded by an external foil conductor and protected by insulation layers. These two conductors are separated by an insulating dielectric. This cable is commonly used for TV cables because its performance is more stable than a twisted-pair (telecommunication) cable.
Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optic cable transmits signals through a strand of glass fiber and, due to having higher bandwidth than other metallic cable types, can carry more information and data. Because of this feature, despite its high cost, it is used instead of copper cables.
Which Wire and Cable Are Suitable for Different Uses?
Which Wire and Cable Are Suitable for Residential Building Wiring?
In residential electrical wiring, flexible stranded and solid wires with a cross-sectional area of 1.5 to 4 mm² are usually used. Flexible stranded wires are very suitable for pulling through electrical conduits due to greater flexibility, while solid wires are used for straight and fixed routes. For outlets, 2.5 mm² wire is often used, and for lighting, 1.5 mm² wire is used.
Which Wire and Cable Are Suitable for Workshops and Factories?
Workshops and factories, due to heavy loads and industrial machinery, need cables with larger cross-sectional areas and stronger insulation. NYY or N2XY cables with PVC or XLPE insulation are very common for these environments. In cases where earthing is essential, three-core and four-core cables are used. Also, for environments with mechanical hazards or oil exposure, using shielded and armored cables is recommended.
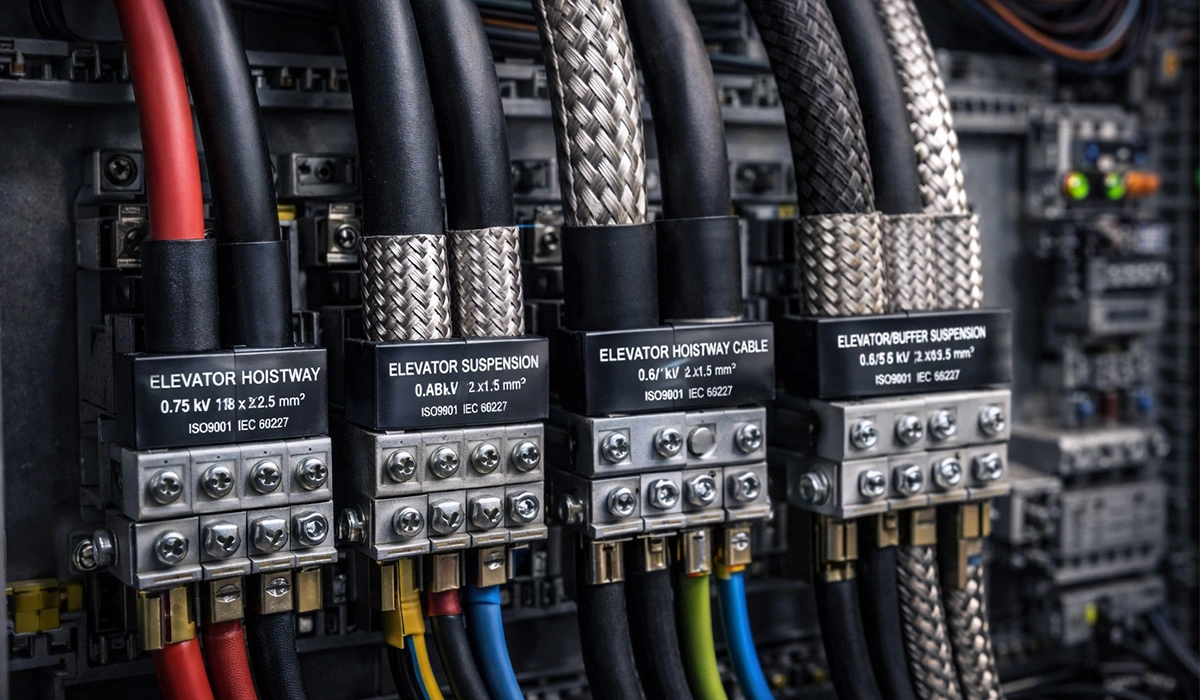

Which Wire and Cable Are Suitable for Elevators and Hoists?
For elevators, flat (Flat) or special flexible elevator cables must be used. These cables are designed to bend and straighten easily during continuous movement without being damaged. Elevator control cables usually have a durable PVC sheath and sometimes shielding to reduce electromagnetic noise. The cross-sectional area must be selected according to the elevator motor current and auxiliary equipment.
Which Wire and Cable Are Suitable for Lighting and Low-Power Equipment?
For lighting and low-power home and office equipment, flexible stranded wires with a cross sectional area of 1 to 1.5 mm² are sufficient. These wires are easy to install in electrical conduits and have lower cost. Lightweight surface cables such as two-core NYM cable are also used in some projects. Compliance with standards in this area is very important to prevent risks caused by voltage drop or fire.
Which Wire and Cable Are Suitable for Air Conditioners and High-Consumption Home Appliances?
Air conditioners, electric heaters, and other high-consumption appliances require wires with larger cross-sectional areas. For air conditioners, 3×4 or 3×6 mm² is usually recommended depending on the device capacity. Using low-quality wires and cables in this section can lead to overheating and fire risk. Flexible stranded cables with heat-resistant insulation are the best option for these consumers.
Which Wire and Cable Are Suitable for Telecommunication and Network Systems?
For telecommunications and networks, twisted pair cables such as CAT5e, CAT6, and CAT7 are used. These cables are designed to reduce electromagnetic noise and signal interference. In traditional telephone systems, multi-pair cables with PVC or PE sheath are used. In industrial environments, shielded network cables (STP/FTP) are recommended.
Which Wire and Cable Are Suitable for CCTV Systems?
Analog CCTV cameras require coaxial cables such as RG59 or RG6 to transmit video signals without quality loss. For IP cameras, CAT5e or CAT6 cables are recommended. When distances are long, fiber optic cables are an ideal option for data transmission. Also, for powering cameras, a two-core power cable is usually used alongside the video cable.
Which Wire and Cable Are Suitable for Outdoor and Humid Environments?
In outdoor, humid, or soil-contact environments, cables with sheath resistant to UV, moisture, and mechanical pressure must be used. NYY and N2XY cables or armored cables are very suitable for direct burial in soil. In wet environments such as pools and sheds, cables with XLPE or PE sheath are also a good option.
Which Wire and Cable Are Suitable for Data Centers and IT Equipment?
In data centers where cable density is high, high-quality network cables (CAT6A or CAT7) and, in some cases, fiber optics should be used. Also, for powering racks and servers, copper flexible stranded cables with heat-resistant and low-smoke insulation (LSZH) are used. LSZH cables, due to producing less smoke and toxic gas during fire, are a standard choice for data centers.
Which Wire and Cable Are Suitable for Solar Systems?
In solar systems, special PV Solar Cables must be used. These cables have XLPE or EPR sheath resistant to UV radiation, high temperatures, and harsh weather conditions. Solar cables usually have special standards such as TÜV and their lifespan is more than 25 years outdoors. Using ordinary cables in solar systems reduces efficiency and increases the risk of early failure.
If you found this article useful, reading an article on topic Solar Systems is recommended for more specialized information.
Conclusion
Selecting the right wire or cable depends on voltage level, conductor type, insulation, protection needs, and how the cable will be installed and used. Using proper standards, correct cross-sectional sizing, and the right cable structure for each environment helps prevent overheating, voltage drop, and fire risks while improving reliability and service life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is using non-standard wire and cable dangerous?
Yes, it leads to higher losses, overheating, and fire risk.
What wire cross-sectional area is suitable for an air conditioner?
Depending on capacity, usually 4 to 6 mm².
Are CAT5e network cables still used?
Yes, but for higher speeds, CAT6 and CAT7 are recommended.
What is different about solar-specific cables?
They have insulation resistant to UV, heat, and moisture, and a longer lifespan.
Why is flat cable used for elevators?
Because of high flexibility and the ability to withstand continuous elevator movement.